MAX16059 Overview
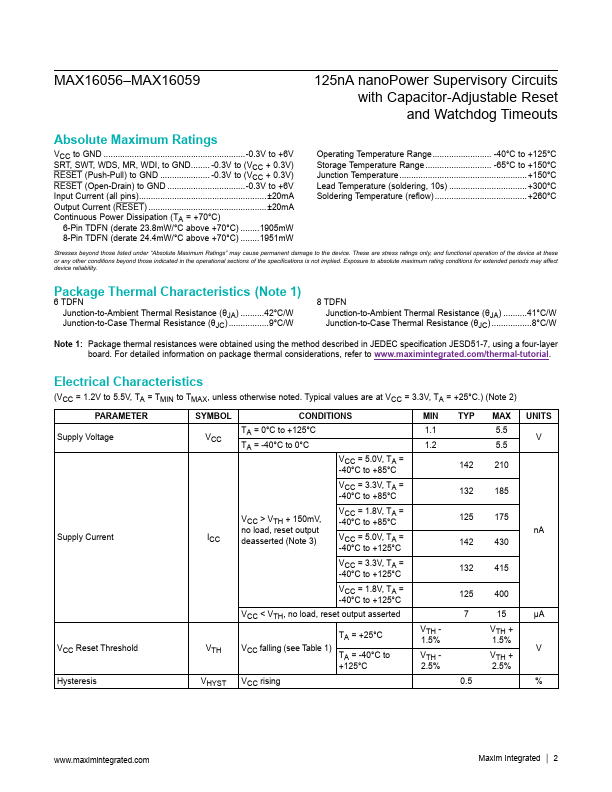
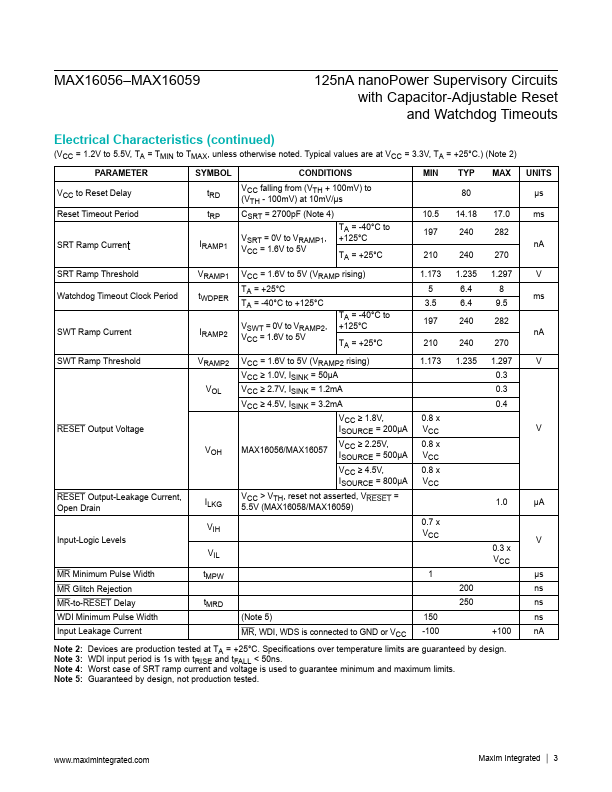
The MAX16056 MAX16059 are ultra-low-current 125nA (typ) microprocessor (µP) supervisory circuits that monitor a single system supply voltage. These devices assert an active-low reset signal whenever the V CC supply voltage drops below the factory-trimmed reset threshold, manual reset is pulled low, or the watchdog timer runs out (MAX16056/MAX16058). The reset output remains asserted for an adjustable reset timeout...