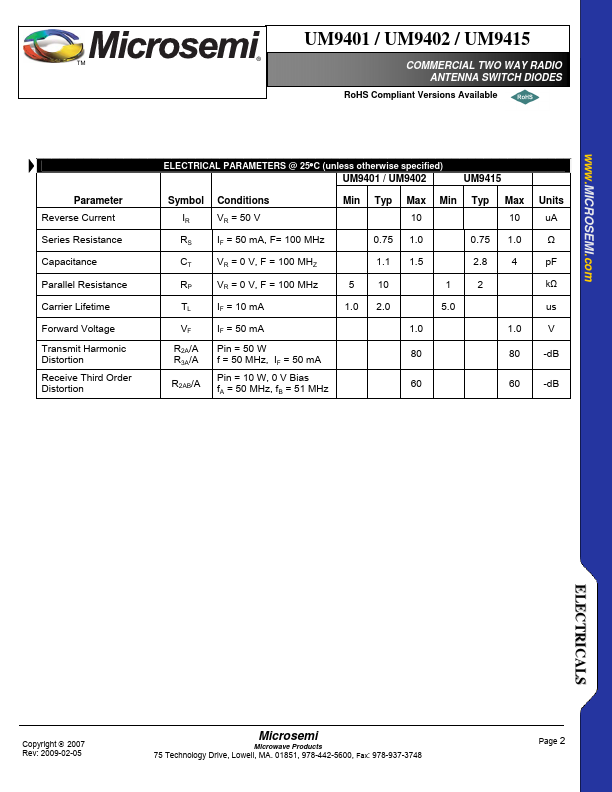
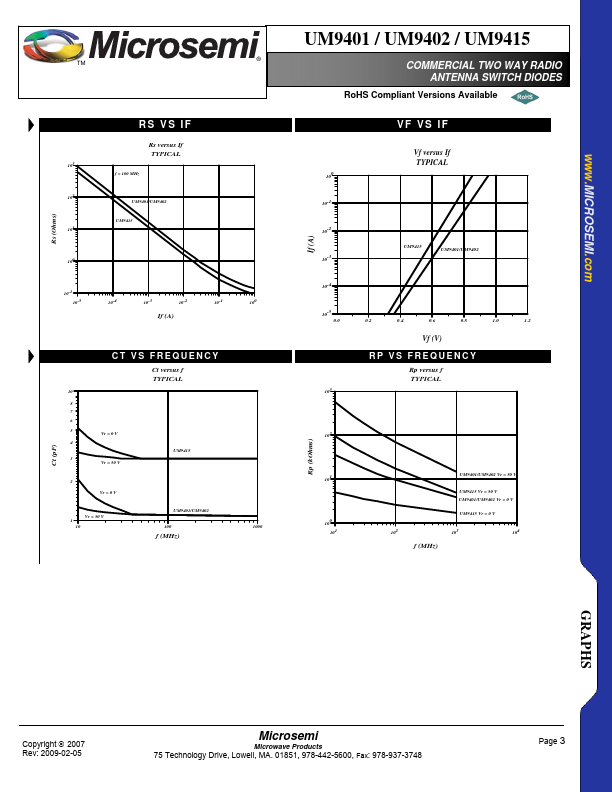
UM9415 Description
Microsemi offers a series of PIN diodes specifically designed and characterized for solid state antenna switches in mercial two-way radios. Antenna switches using the UM9401 and UM9415 series PIN diodes provide high isolation, low loss and low distortion characteristics formerly possible only with electromechanical relay type switches. The UM9401 and the UM9402 diodes can handle 100 W of transmitter power, while the...
UM9415 Key Features
- High transmitter power
- Low harmonic distortion
- Low third order distortion
- High carrier lifetime
- Non cavity design
- Thermally matched configuration
- Low capacitance at 0 V bias
- Low conductance at 0 V bias
- patible with automatic
- RoHS plaint versions