M21554 Description
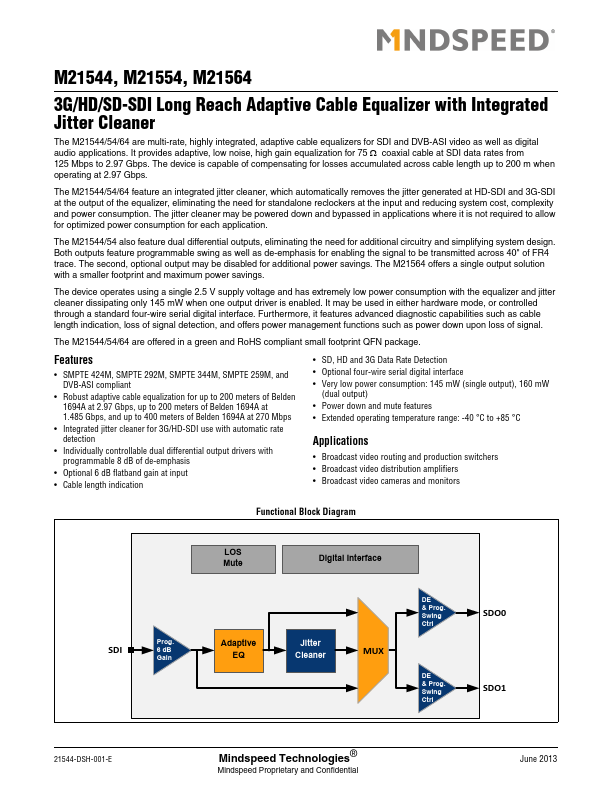
M21544, M21554, M21564 3G/HD/SD-SDI Long Reach Adaptive Cable Equalizer with Integrated Jitter Cleaner The M21544/54/64 are multi-rate, highly integrated, adaptive cable equalizers for SDI and DVB-ASI video as well as digital audio applications. It provides adaptive, low noise, high gain equalization for 75 coaxial cable at SDI data rates from 125 Mbps to 2.97 Gbps. The device is capable of pensating for losses...
M21554 Key Features
- SMPTE 424M, SMPTE 292M, SMPTE 344M, SMPTE 259M, and DVB-ASI pliant
- Integrated jitter cleaner for 3G/HD-SDI use with automatic rate detection
- Individually controllable dual differential output drivers with programmable 8 dB of de-emphasis
- Optional 6 dB flatband gain at input
- Cable length indication
- SD, HD and 3G Data Rate Detection
- Optional four-wire serial digital interface
- Very low power consumption: 145 mW (single output), 160 mW
- Power down and mute features
- Extended operating temperature range: -40 °C to +85 °C