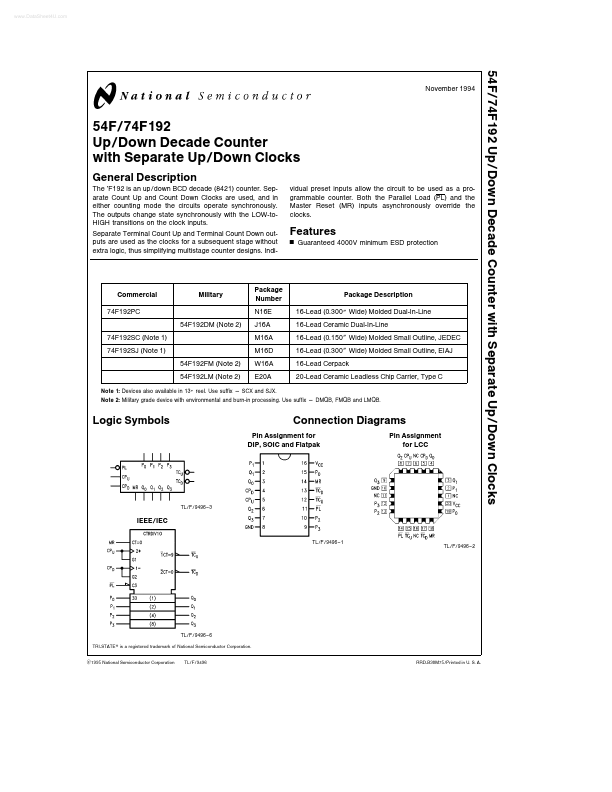
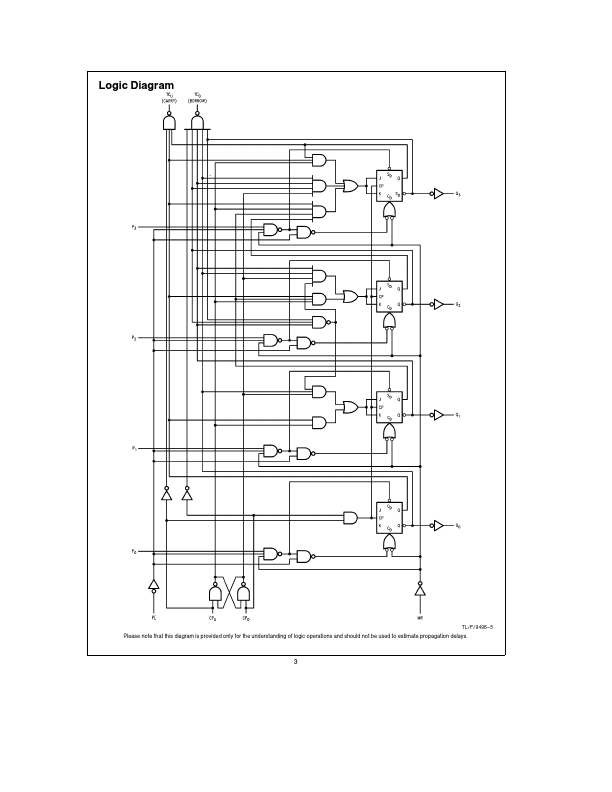
74F192 Overview
The ’F192 is an up down BCD decade (8421) counter Separate Count Up and Count Down Clocks are used and in either counting mode the circuits operate synchronously The outputs change state synchronously with the LOW-toHIGH transitions on the clock inputs Separate Terminal Count Up and Terminal Count Down outputs are used as the clocks for a subsequent stage without extra logic thus simplifying multistage counter...
74F192 Key Features
- Q3 TCD TCU