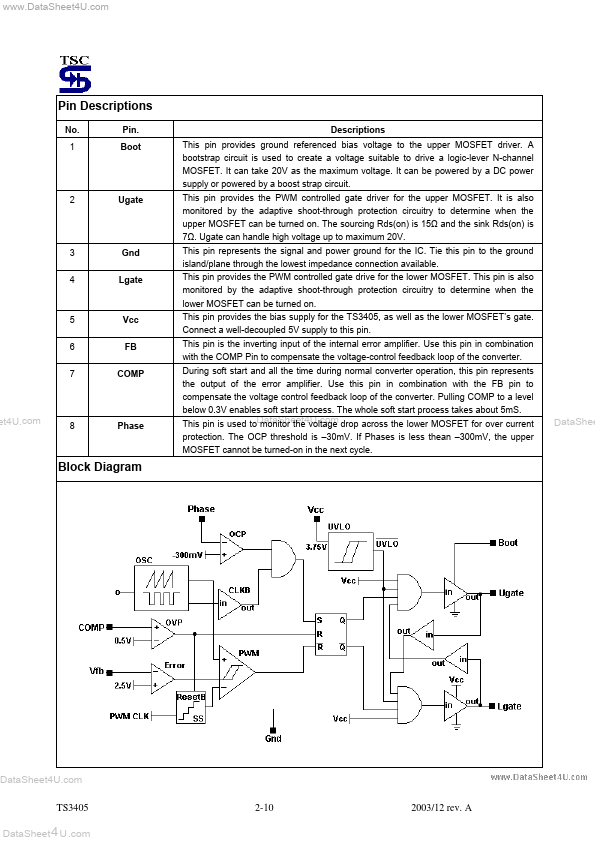
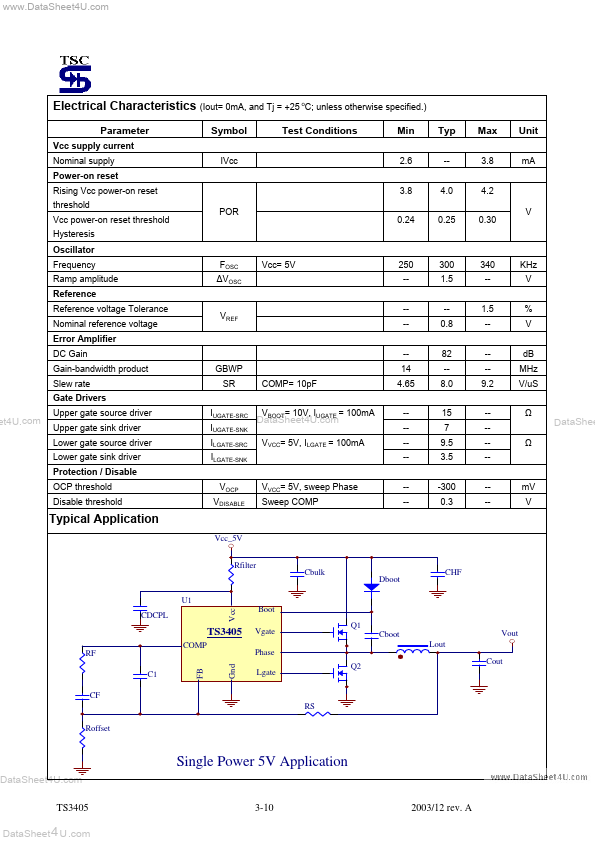
TS3405 Overview
The TS3405 makes simple work out of implementing a plete control and protection scheme for a DC-DC step-down converter. Designed to drive N-channel MOSFETs in a synchronous buck topology, the TS3405 integrates the control, output a adjustment, monitoring and protection functions. The TS3405 provides simple, single feedback loop, voltage mode control with fast transient response.