MAX15106C Overview
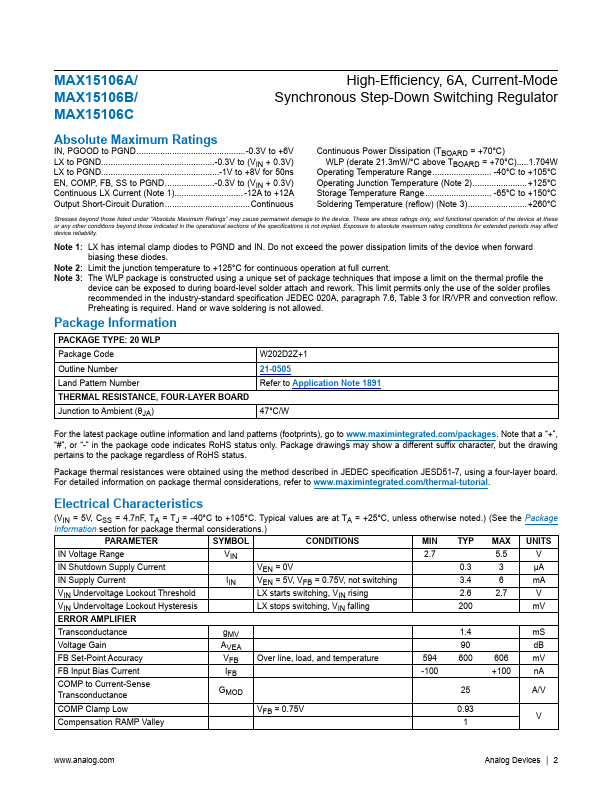
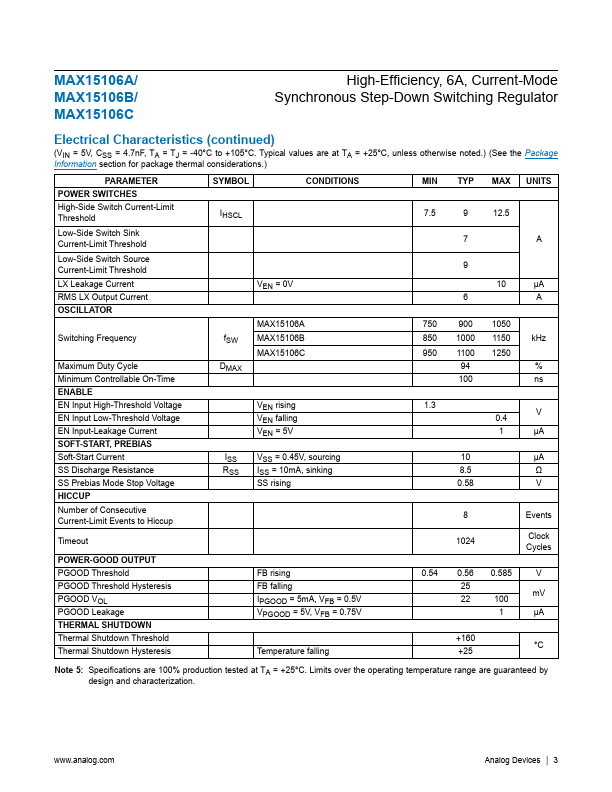
The MAX15106A/MAX15106B/MAX15106C family of high-efficiency, current-mode, synchronous step-down switching regulators with integrated power switches deliver up to 6A of output current. The regulators operate from 2.7V to 5.5V and provide an output voltage from 0.6V up to 95% of the input voltage, making the devices ideal for distributed power systems, portable devices, and preregulation applications. The ICs utilize...
MAX15106C Key Features
- Continuous 6A Output Current
- Efficiency Up to 96%
- ±1% Accuracy Over Load, Line, and Temperature
- Operates from a 2.7V to 5.5V Supply
- Adjustable Output from 0.6V to 0.95 × VIN
- Programmable Soft-Start
- Safe Startup into Prebiased Output
- External Reference Input
- 0.9MHz, 1.0MHz, and 1.1MHz Switching Frequency
- Stable with Low-ESR Ceramic Output Capacitors