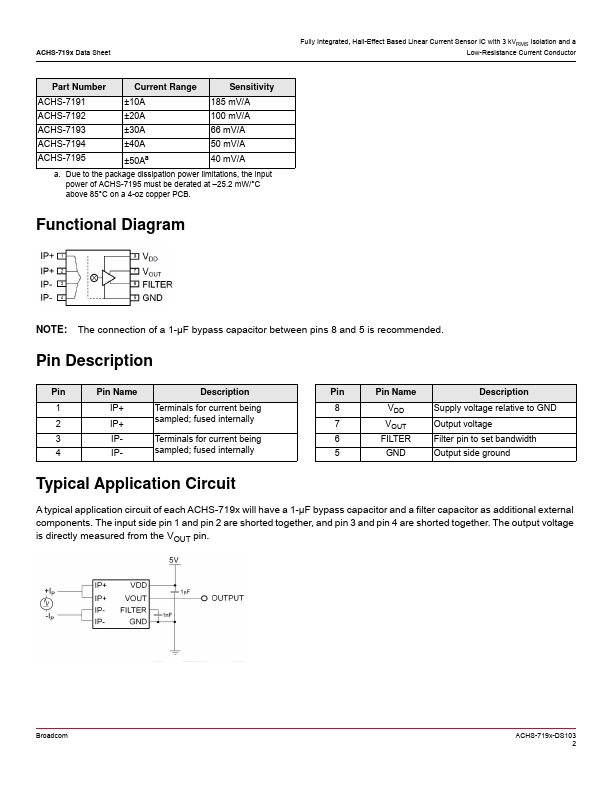
ACHS-7191 Description
The Broad® ACHS-719x (±10A to ±50A) fully integrated Hall-effect based isolated linear current sensors are designed for AC or DC current sensing in industrial, mercial, and munications systems. Inside each ACHS-719x IC is a precise, low-offset, linear Hall circuit with a copper conduction path located near the surface of the die. Applied current flowing through this copper conduction path generates a magnetic field...
ACHS-7191 Key Features
- Wide operating temperature: -40ºC to +110ºC
- Internal conductor resistance: 0.7 mΩ typ
- Sensing current range: ± 10A ~ ± 50A
- Output sensitivity: 40 mV/A to 185 mV/A
- Output voltage proportional to AC or DC currents
- Ratiometric output from supply voltage
- Single supply operation: 5.0V
- Low-noise analog signal path
- Device bandwidth is set via the new FILTER pin
- 80 kHz typ. bandwidth with 1-nF filter capacitor