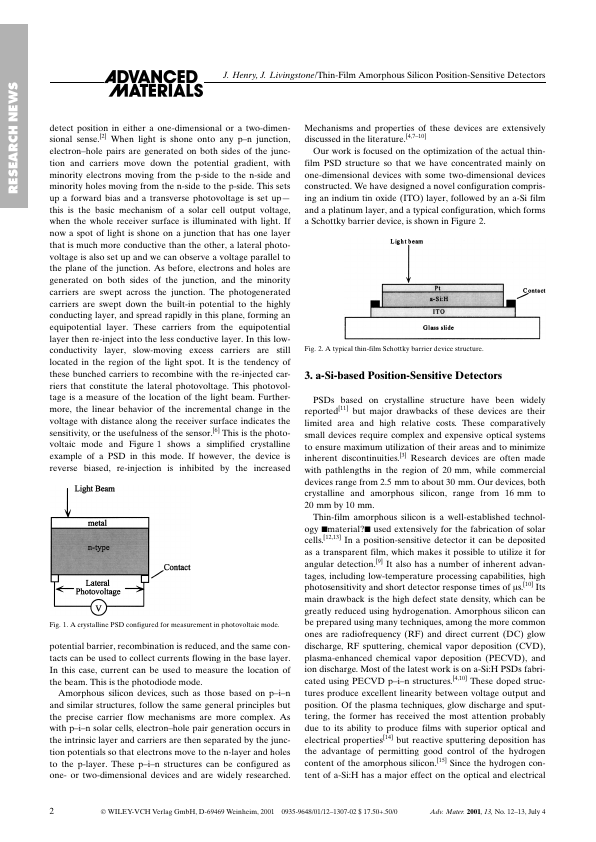
RN552 Description
RESEARCH NEWS Thin-Film Amorphous Silicon Position-Sensitive Detectors By Jasmine Henry and John Livingstone Optical position-sensitive detectors are a useful class of sensor with a wide range of applications in machine control systems, industrial alignment and robotic vision. They have distinct advantages over most arrayed discrete optical devices in that they can produce continuous optical signals, and versions...