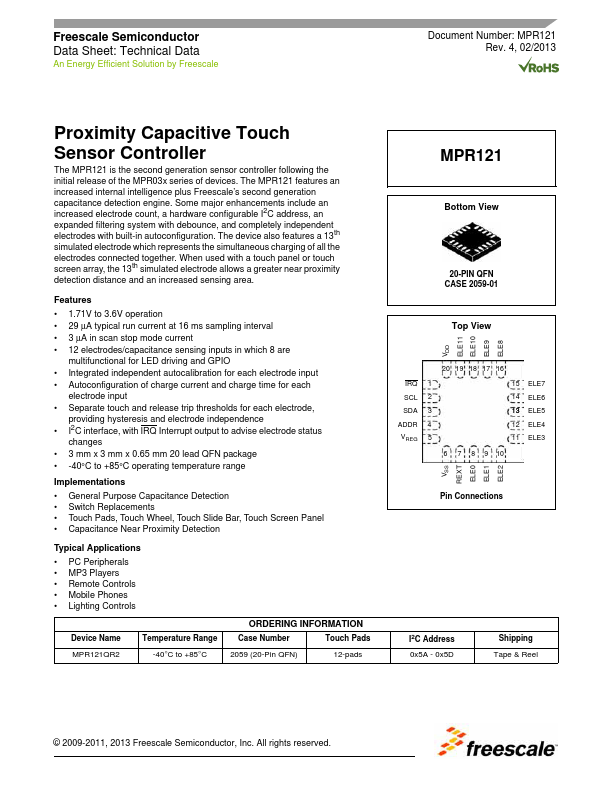
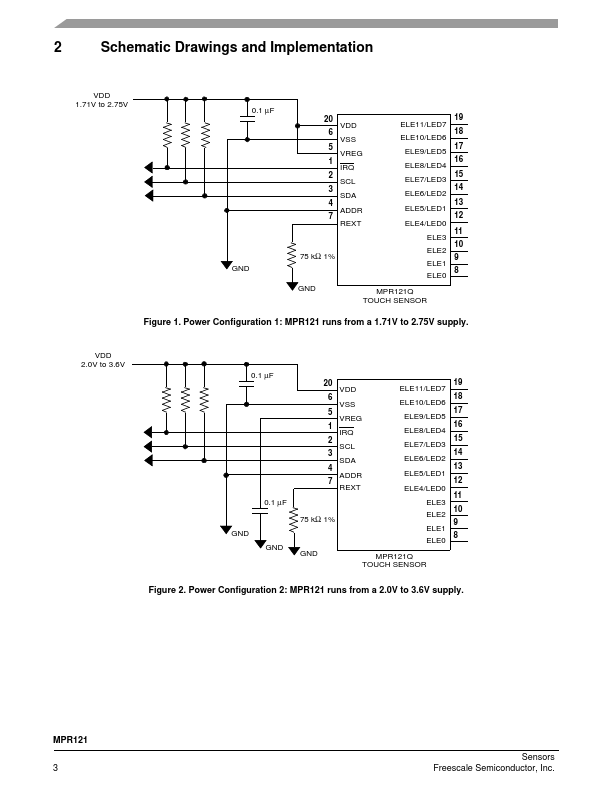
MPR121QR2 Overview
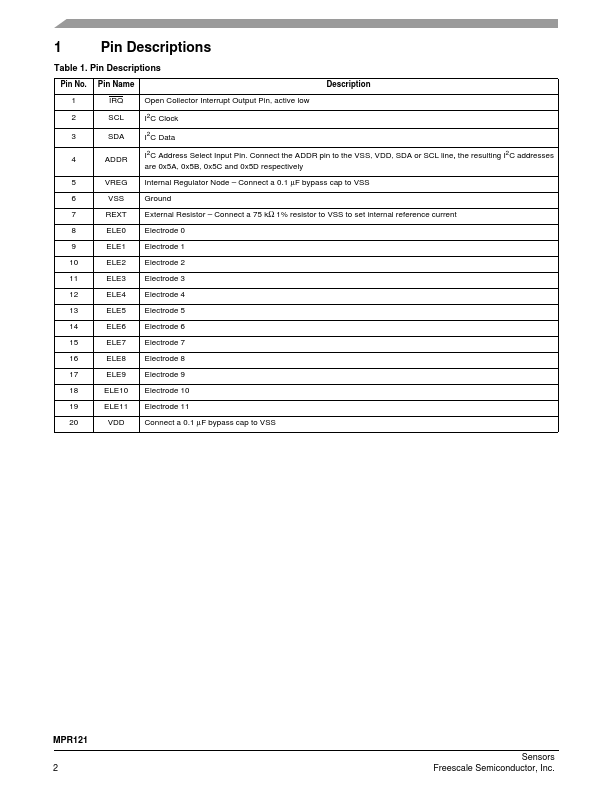
1 IRQ Open Collector Interrupt Output Pin, active low 2 SCL I2C Clock 3 SDA I2C Data 4 ADDR I2C Address Select Input Pin.
MPR121QR2 Key Features
- 1.71V to 3.6V operation
- 29 μA typical run current at 16 ms sampling interval
- 3 μA in scan stop mode current
- 12 electrodes/capacitance sensing inputs in which 8 are
- Integrated independent autocalibration for each electrode input
- Autoconfiguration of charge current and charge time for each
- Separate touch and release trip thresholds for each electrode
- I2C interface, with IRQ Interrupt output to advise electrode status
- 3 mm x 3 mm x 0.65 mm 20 lead QFN package
- 40°C to +85°C operating temperature range