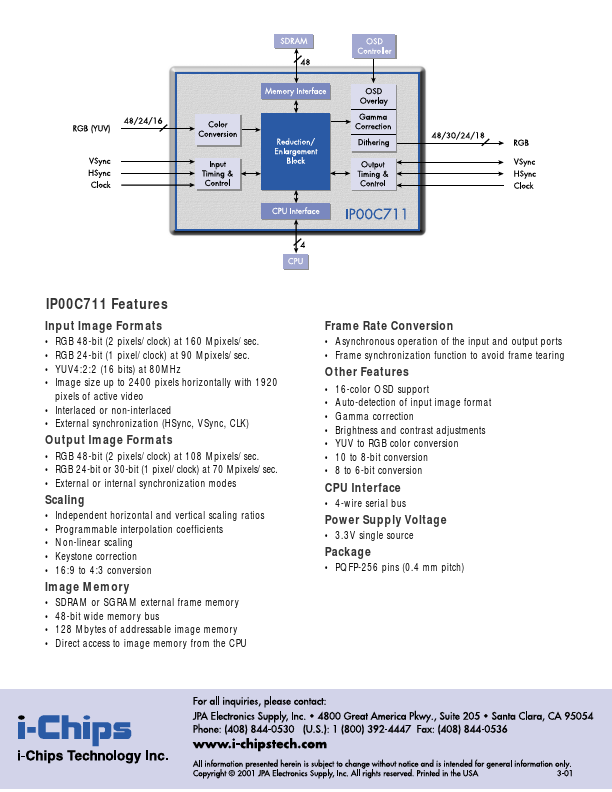
IP00C711 Description
The IP00C711 (SCREEN3) is a highly integrated device for real-time color image scaling and frame rate conversion up to SXGA resolution. The IP00C711 supports all the critical functions required in any display control logic: image scaling, frame rate conversion and de-interlacing.
IP00C711 Key Features
- Interlaced or non-interlaced
- External synchronization (HSync, VSync, CLK)
- Asynchronous operation of the input and output ports
- Frame synchronization function to avoid frame tearing
- 16-color OSD support Auto-detection of input image format Gamma correction Brightness and contrast adjustments YUV to RG
- RGB 48-bit (2 pixels/clock) at 108 Mpixels/sec
- RGB 24-bit or 30-bit (1 pixel/clock) at 70 Mpixels/sec
- External or internal synchronization modes
- 4-wire serial bus
- Independent horizontal and vertical scaling ratios Programmable interpolation coefficients Non-linear scaling Keystone c