89HPES16NT2 Description
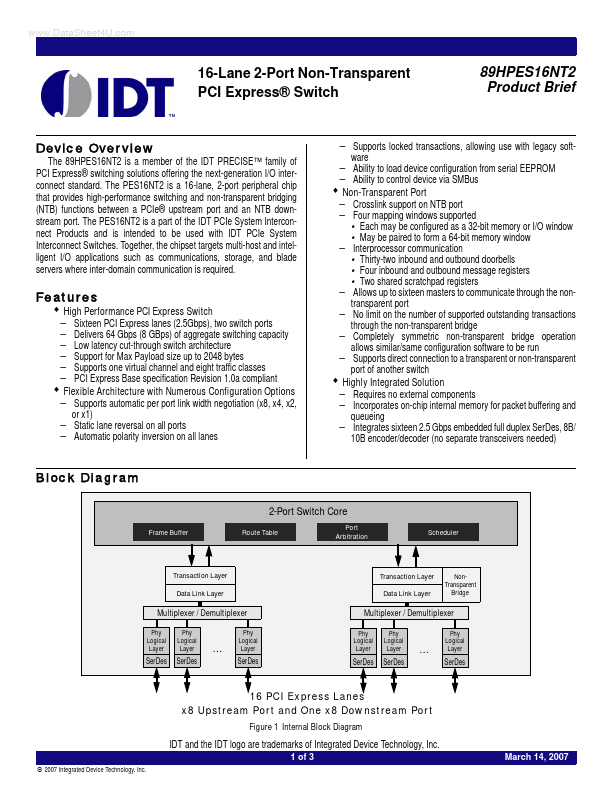
16-Lane 2-Port Non-Transparent PCI Express® Switch 89HPES16NT2 Product Brief Device Overview The 89HPES16NT2 is a member of the IDT PRECISE™ family of PCI Express® switching solutions offering the next-generation I/O interconnect standard. The PES16NT2 is a 16-lane, 2-port peripheral chip that provides high-performance switching and non-transparent bridging (NTB) functions between a PCIe® upstream port and an NTB...
89HPES16NT2 Key Features
- Sixteen PCI Express lanes (2.5Gbps), two switch ports
- Delivers 64 Gbps (8 GBps) of aggregate switching capacity
- Low latency cut-through switch architecture
- Support for Max Payload size up to 2048 bytes
- Supports one virtual channel and eight traffic classes
- PCI Express Base specification Revision 1.0a pliant
- Flexible Architecture with Numerous Configuration Options
- Supports automatic per port link width negotiation (x8, x4, x2, or x1)
- Static lane reversal on all ports
- Automatic polarity inversion on all lanes