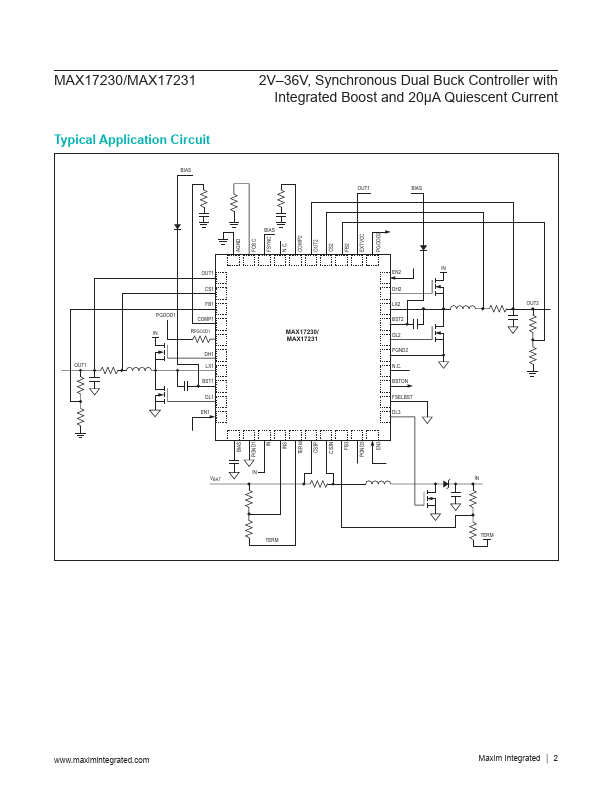
MAX17231 Description
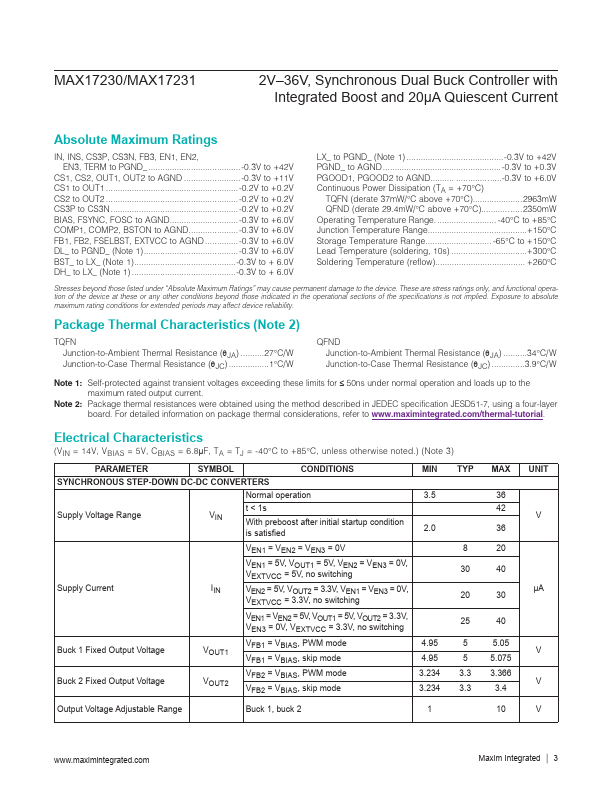
The MAX17230/MAX17231 offers dual synchronous stepdown DC-DC controllers with integrated MOSFETs and a step-up/boost controller. They operate over a 3.5V to 36V input voltage range, and down to 2V with the boost controller active. The devices can operate in dropout condition by running at 95% duty cycle.
MAX17231 Key Features
- Eliminates External ponents and Reduces Total Cost
- No Schottky-Synchronous Operation for High Efficiency and Reduced Cost
- Simple External RC pensation for Stable Operation at Any Output Voltage
- All-Ceramic Capacitor Solution: Ultra-pact Layout
- 180° Out-of-Phase Operation Reduces Output Ripple and Enables Cascaded Power Supplies
- Reduces Number of DC-DC Controllers to Stock
- Fixed Output Voltage with ±1% Accuracy (5V/3.3V) or Externally Resistor Adjustable (1V to 10V)
- 220kHz to 2.2MHz Adjustable Frequency with External Synchronization
- Frequency Synchronization Input
- Reduces Power Dissipation