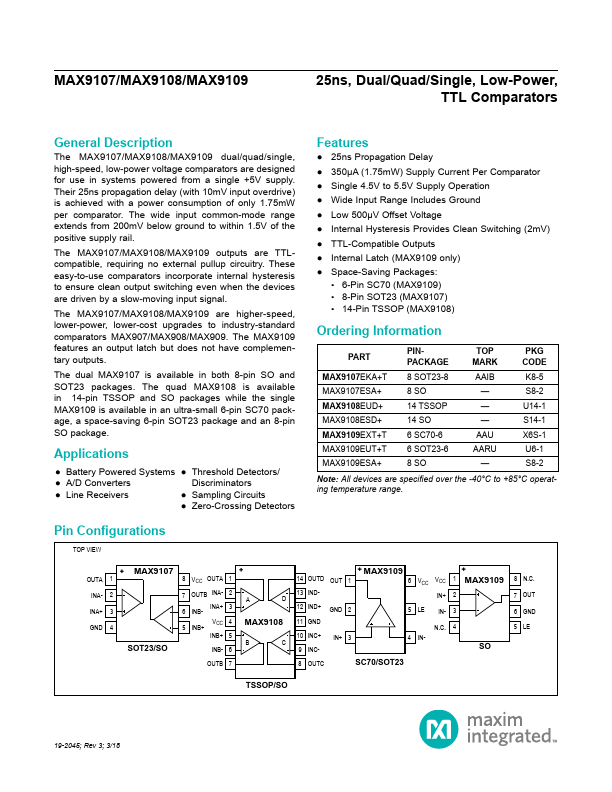
MAX9108 Description
The MAX9107/MAX9108/MAX9109 dual/quad/single, high-speed, low-power voltage parators are designed for use in systems powered from a single +5V supply. Their 25ns propagation delay (with 10mV input overdrive) is achieved with a power consumption of only 1.75mW per parator. The wide input mon-mode range extends from 200mV below ground to within 1.5V of the positive supply rail.