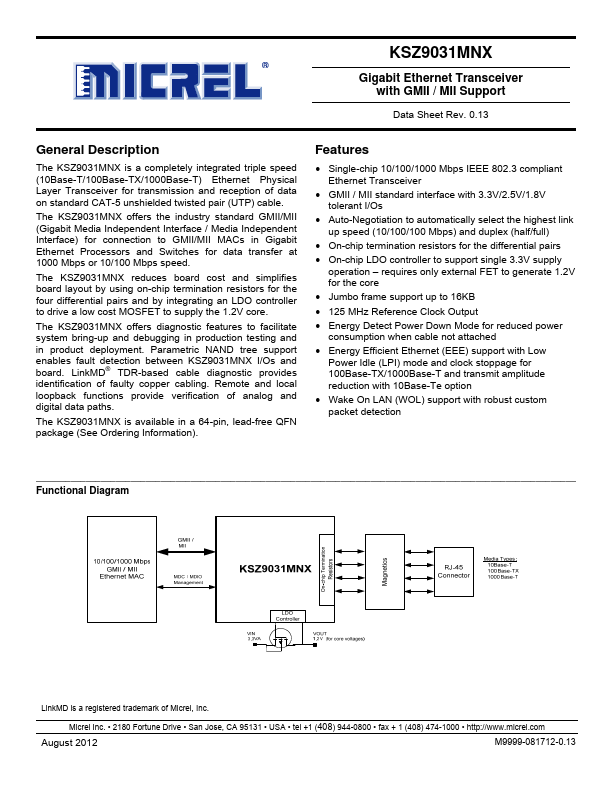
KSZ9031MNX Key Features
- Single-chip 10/100/1000 Mbps IEEE 802.3 pliant Ethernet Transceiver
- GMII / MII standard interface with 3.3V/2.5V/1.8V tolerant I/Os
- Auto-Negotiation to automatically select the highest link up speed (10/100/100 Mbps) and duplex (half/full)
- On-chip termination resistors for the differential pairs
- On-chip LDO controller to support single 3.3V supply operation
- requires only external FET to generate 1.2V for the core
- Jumbo frame support up to 16KB
- 125 MHz Reference Clock Output
- Energy Detect Power Down Mode for reduced power consumption when cable not attached
- Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) support with Low Power Idle (LPI) mode and clock stoppage for 100Base-TX/1000Base-T and