- Part: HAL300
- Description: Differential Hall Effect Sensor IC
- Manufacturer: Micronas
- Size: 126.07 KB
 Page 2
Page 2
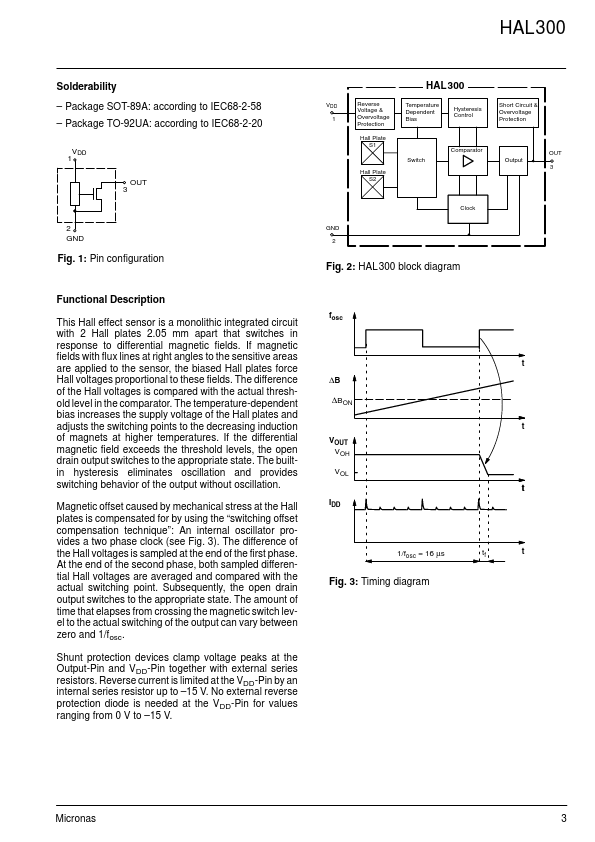 Page 3
Page 3
HAL300 Key Features
- distance between Hall plates: 2.05 mm
- operates from 4.5 V to 24 V supply voltage
- switching offset pensation at 62 kHz
- overvoltage protection
- reverse-voltage protection at VDD-pin
- short-circuit protected open-drain output by thermal
- operates with magnetic fields from DC to 10 kHz
- output turns low with magnetic south pole on branded side of package and with a higher magnetic flux density in sensitiv
- on-chip temperature pensation circuitry minimizes shifts of the magnetic parameters over temperature and supply voltage
- the decrease of magnetic flux density caused by rising temperature in the sensor system is pensated by a built-in negati
Other HAL300 Datasheets
| Manufacturer |
Part Number |
Description |
 LEM
LEM |
HAL300-S
|
Current Transducer |





