UBA2071A Description
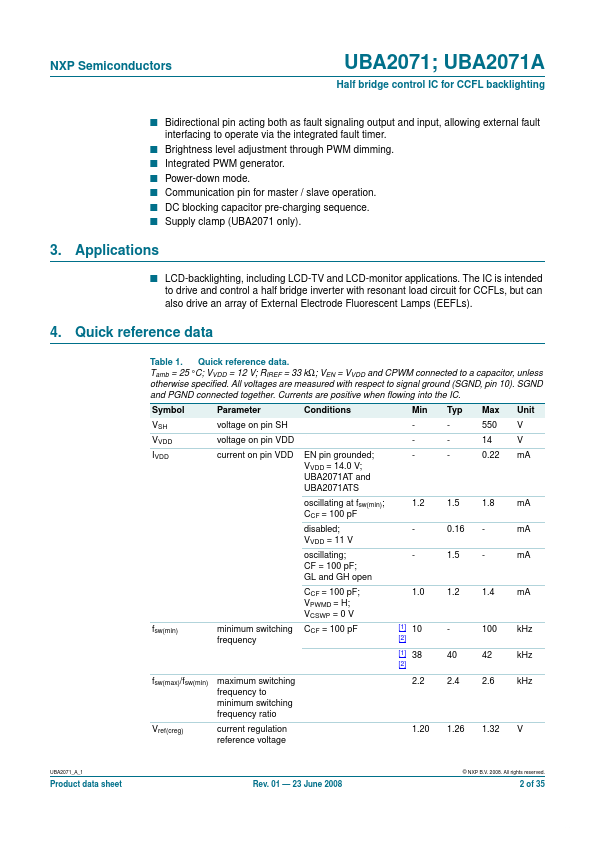
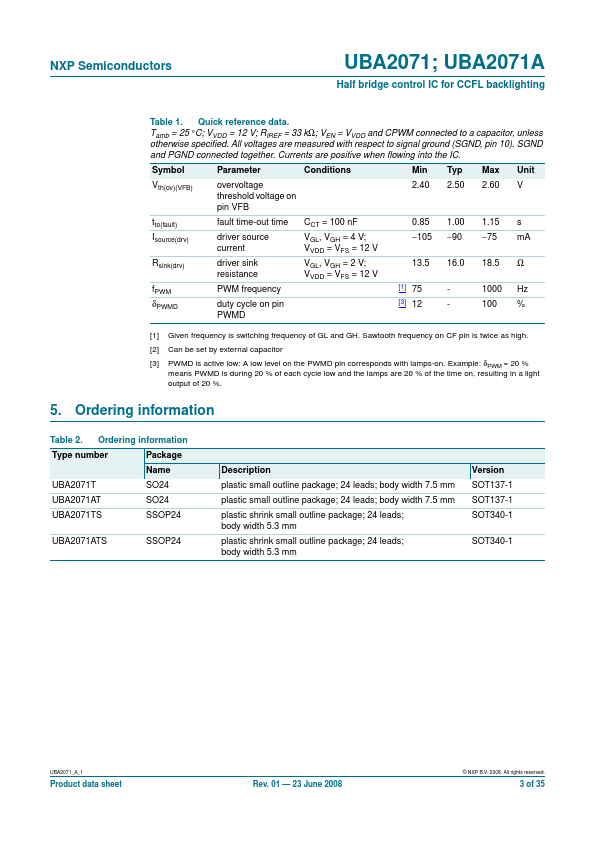
The UBA2071 and UBA2071A are high voltage ICs intended to drive Cold Cathode Fluorescent Lamps (CCFLs) or External Electrode Fluorescent Lamps (EEFLs) for backlighting applications. They can drive a half bridge circuit made up of two NMOSFETs with a supply voltage of up to 550 V, so the inverter can be supplied directly from a 400 V PFC bus. The UBA2071 and UBA2071A contain a controller, a level shifter, a bootstrap...
UBA2071A Key Features
- http://..net/