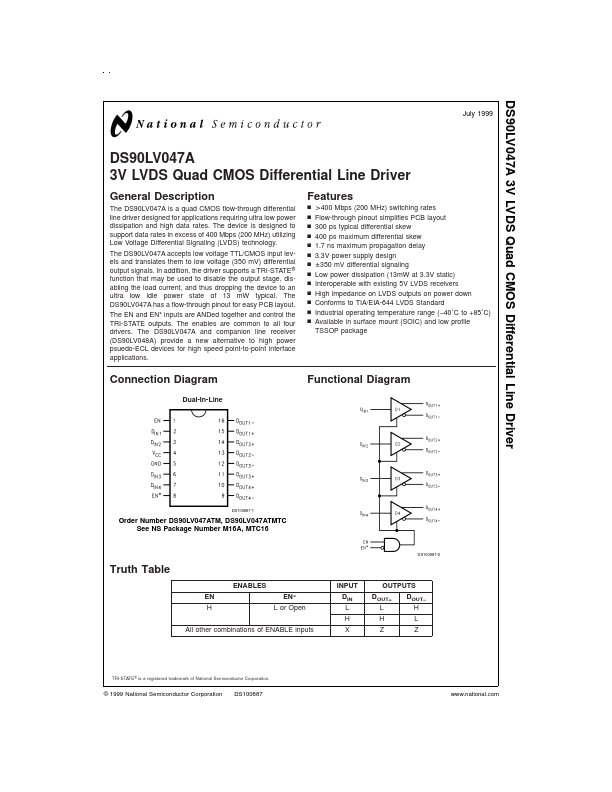
DS90LV047A Description
The DS90LV047A is a quad CMOS flow-through differential line driver designed for applications requiring ultra low power dissipation and high data rates. The device is designed to support data rates in excess of 400 Mbps (200 MHz) utilizing Low Voltage Differential Signaling (LVDS) technology. The DS90LV047A accepts low voltage TTL/CMOS input levels and translates them to low voltage (350 mV) differential output...