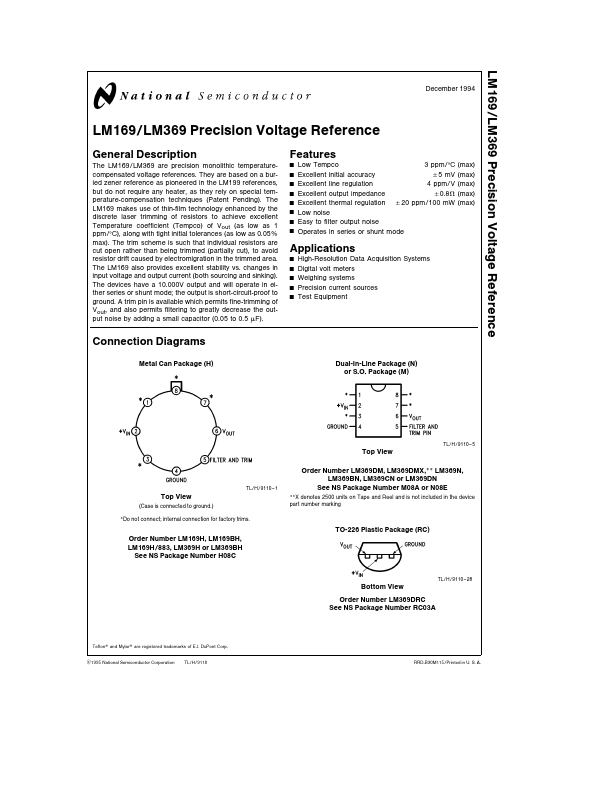
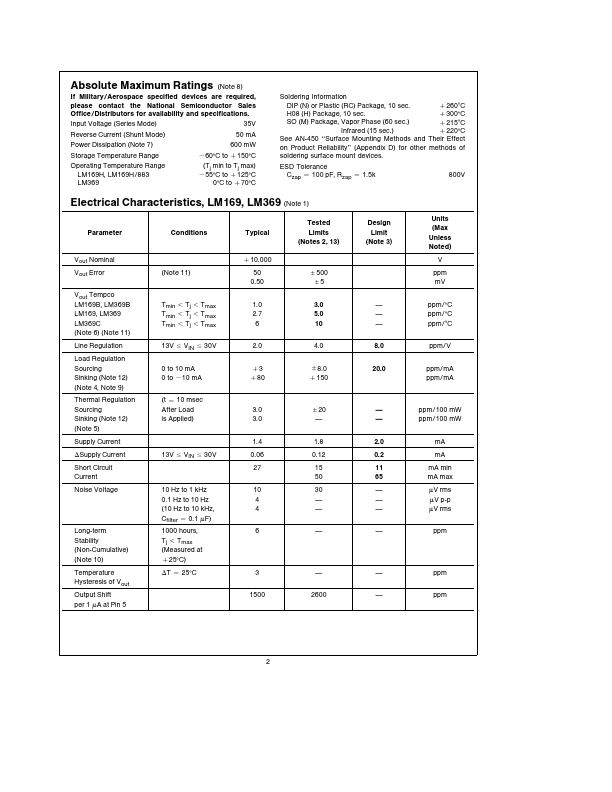
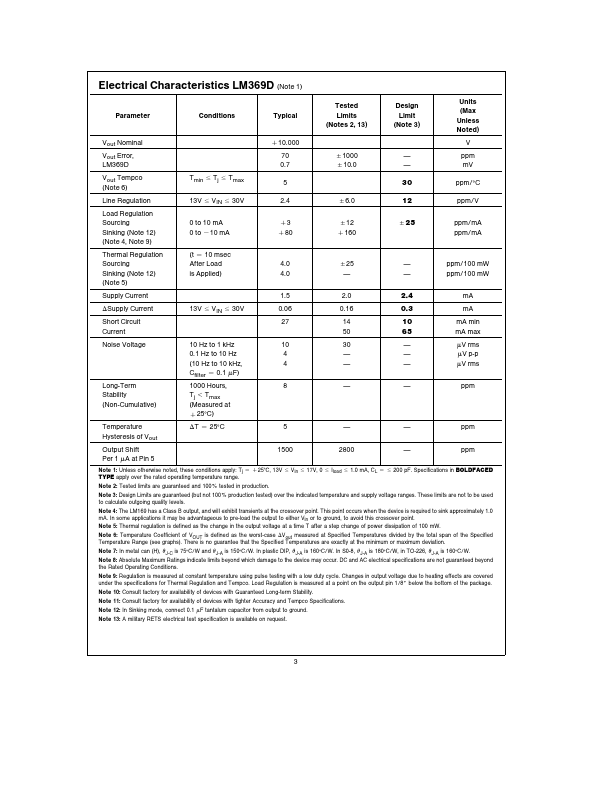
LM369 Description
The LM169 LM369 are precision monolithic temperaturepensated voltage references They are based on a buried zener reference as pioneered in the LM199 references but do not require any heater as they rely on special temperature-pensation techniques (Patent.