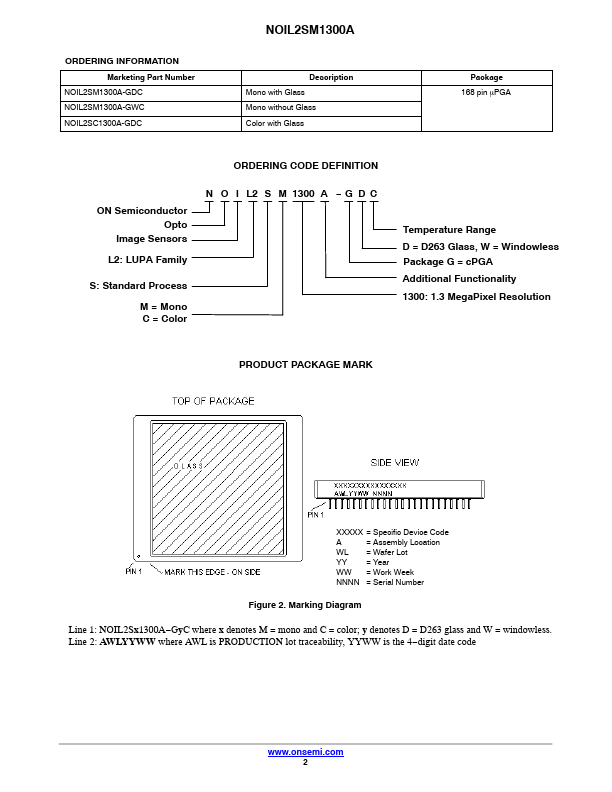
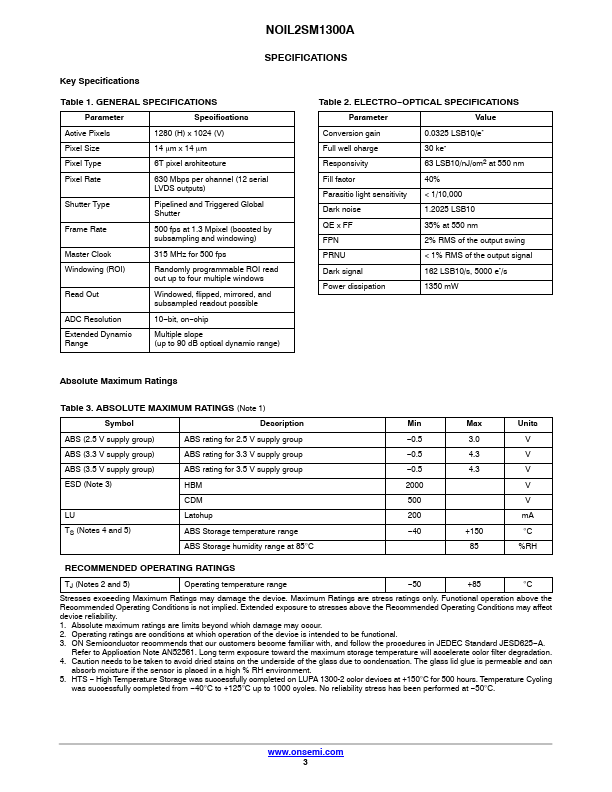
NOIL2SC1300A-GDC Description
Medical Imaging Industrial Imaging Figure 1. LUPA1300−2 Die Photo The LUPA1300-2 is an integrated SXGA high speed, high sensitivity CMOS image sensor. This sensor targets high speed machine vision and industrial monitoring applications.