HD74HC534 Description
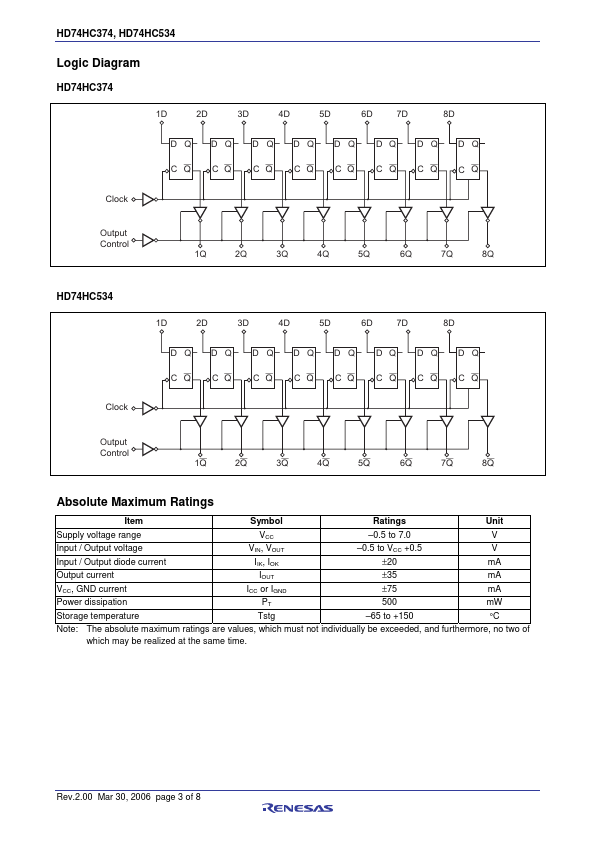
These devices are positive edge triggered flip-flops. The difference between HD74HC374 and HD74HC534 is only that the former is a true outputs and the latter is a false outputs. Data at the D inputs, meeting the setup and hold time requirements, are transferred to the Q outputs on positive going transitions of the clock (CK) input.
HD74HC534 Key Features
- High Speed Operation: tpd (Clock to Q) = 18 ns typ (CL = 50 pF)
- High Output Current: Fanout of 15 LSTTL Loads
- Wide Operating Voltage: VCC = 2 to 6 V
- Low Input Current: 1 µA max
- Low Quiescent Supply Current: ICC (static) = 4 µA max (Ta = 25°C)
- Ordering Information
- EL (2,000 pcs/reel)