LN8542 Overview
The LN8542 (dual) is rail-to-rail input and output voltage feedback amplifier offering low cost. It has a wide input mon-mode voltage range and output voltage swing, and takes the minimum operating supply voltage down to 2.1V and the maximum remended supply voltage is 5.5V. All are specified over the extended 40°C to +125°C temperature range.
LN8542 Key Features
- Low cost
- Rail-to-Rail input / output
- Unity-gain stable
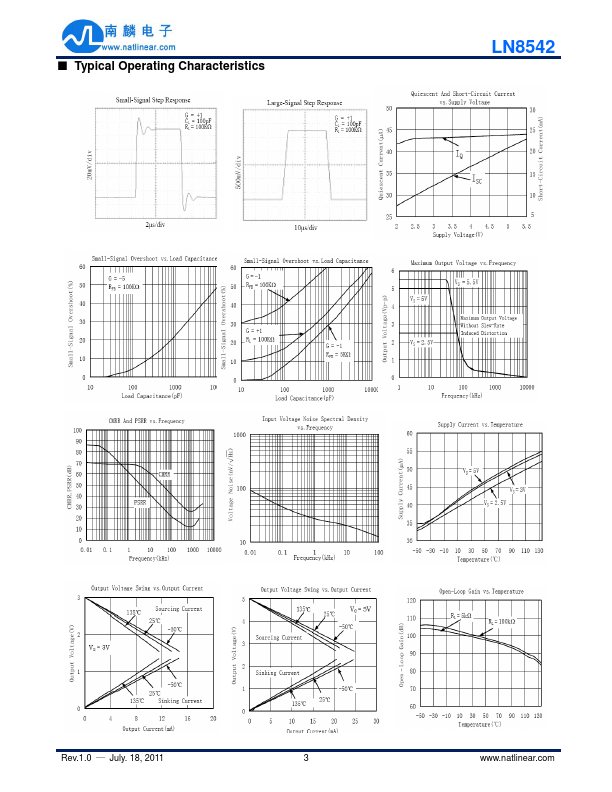
- Slew rate: 0.52 (V/μs)
- Minimum power supply rejection ratio: 72dB
- Minimum mon mode rejection ratio: 76dB
- Offset voltage: typically 0.8mV, 3.5mV maximum
- Gain bandwidth product: 1.1MHz
- Very low input bias current: 0.5pA
- Operating voltage range: 2.1V to 5.5V