IRF3704ZCL Description
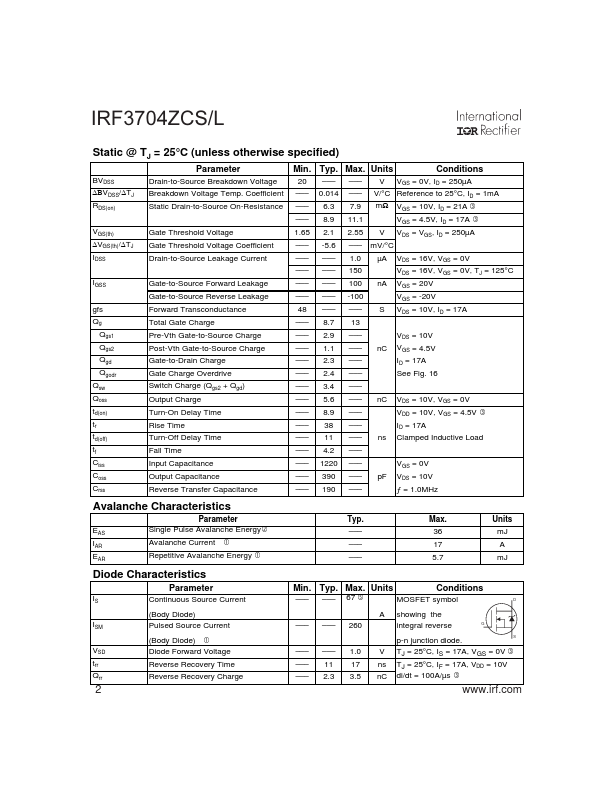
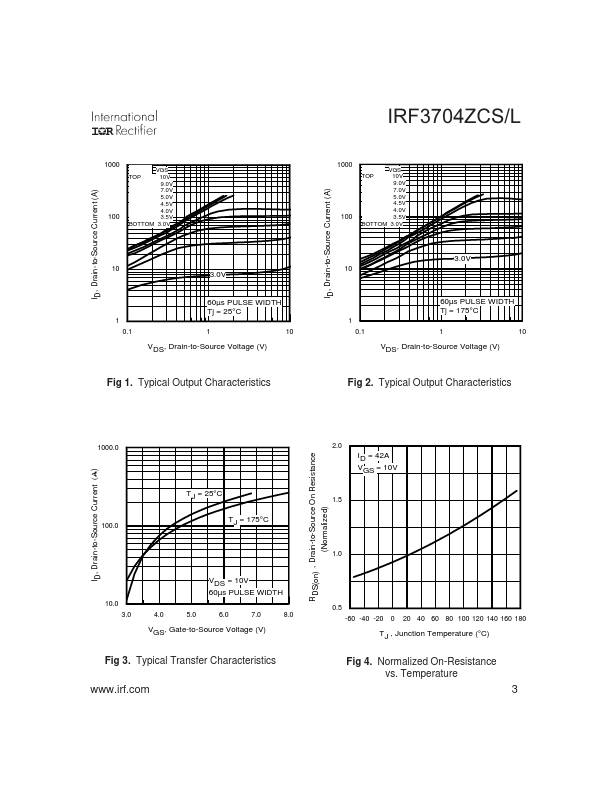
PD - 94782 IRF3704ZCS IRF3704ZCL Applications l High Frequency Synchronous Buck Converters for puter Processor Power HEXFET® Power MOSFET VDSS RDS(on) max 20V 7.9m: 2.65 40 Units °C/W f Notes through are on page 11 .irf. 1 9/15/03 IRF3704ZCS/L Static @ TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise specified) Parameter BVDSS ∆ΒVDSS/∆TJ RDS(on) VGS(th) ∆VGS(th)/∆TJ IDSS IGSS gfs Qg Qgs1 Qgs2 Qgd Qgodr Qsw Qoss td(on) tr td(off) tf...
IRF3704ZCL Key Features
- High Frequency Synchronous Buck Converters for puter Processor Power HEXFET® Power MOSFET VDSS RDS(on) max 2
- Low RDS(on) at 4.5V VGS
- Ultra-Low Gate Impedance
- Fully Characterized Avalanche Voltage and Current D2Pak IRF3704ZCS TO-262 IRF3704ZCL