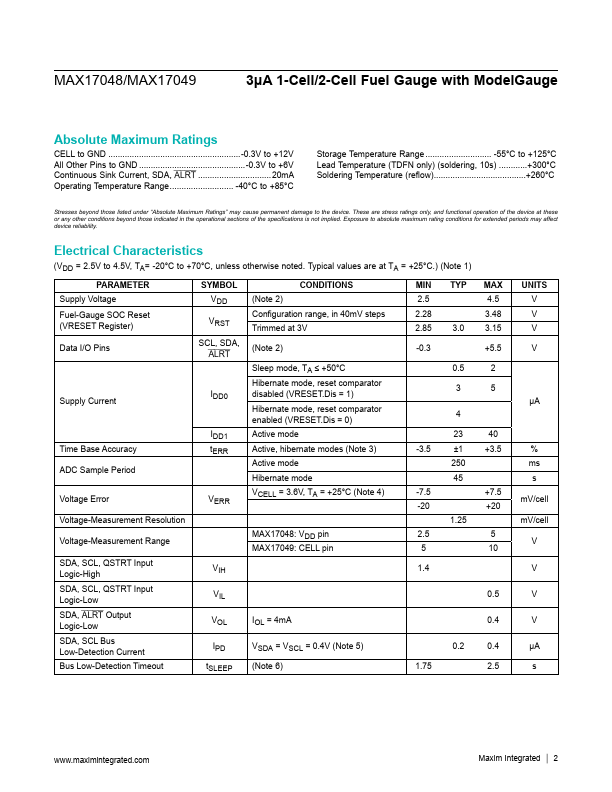
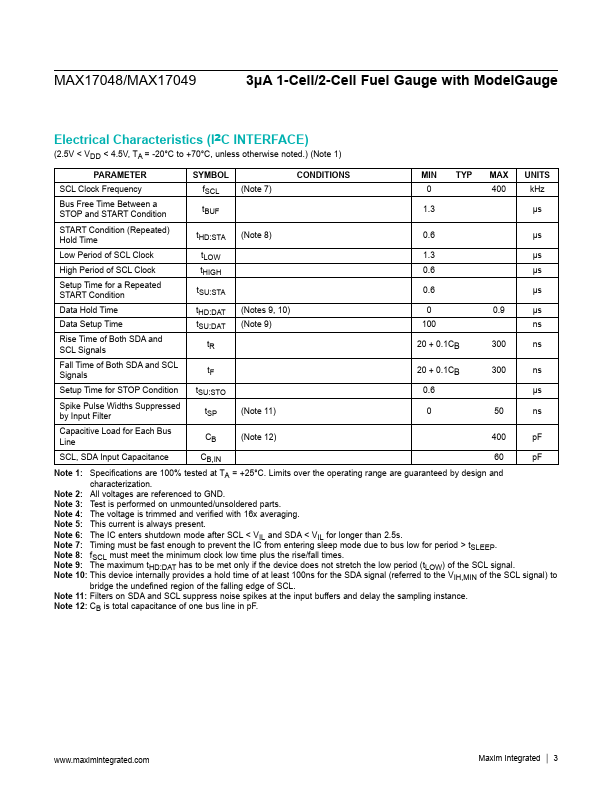
MAX17049 Description
The MAX17048/MAX17049 ICs are tiny, micropower current fuel gauges for lithium-ion (Li+) batteries in handheld and portable equipment. The MAX17048 operates with a single lithium cell and the MAX17049 with two lithium cells in series. The ICs use the sophisticated Li+ battery-modeling algorithm ModelGaugeK to track the battery relative state-of-charge (SOC) continuously over widely varying charge and discharge...
MAX17049 Key Features
- Provides Accurate State-of-Charge
- pensates for Temperature/Load Variation
- Does Not Accumulate Errors, Unlike Coulomb
- Eliminates Learning
- Eliminates Current-Sense Resistor S Ultra-Low Quiescent Current
- 4µA Hibernate, 23µA Active
- Fuel Gauges in Hibernate Mode
- Automatically Enters and Exits Hibernate Mode S Reports Charge and Discharge Rate S Battery-Insertion Debounce
- Best of 16 Samples to Estimate Initial SOC S Programmable Reset for Battery Swap
- 2.28V to 3.48V Range S Configurable Alert Indicator