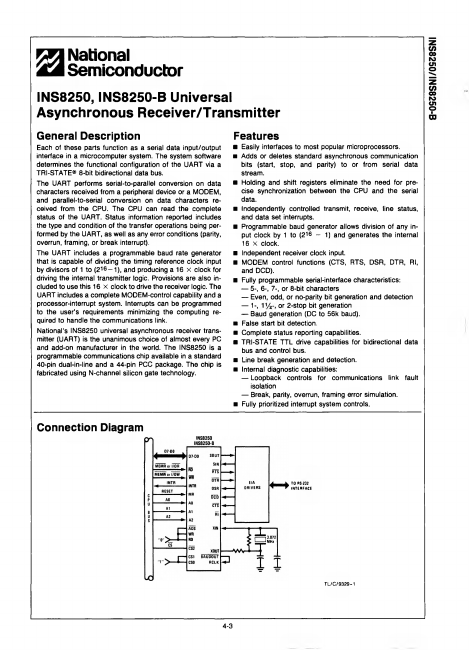
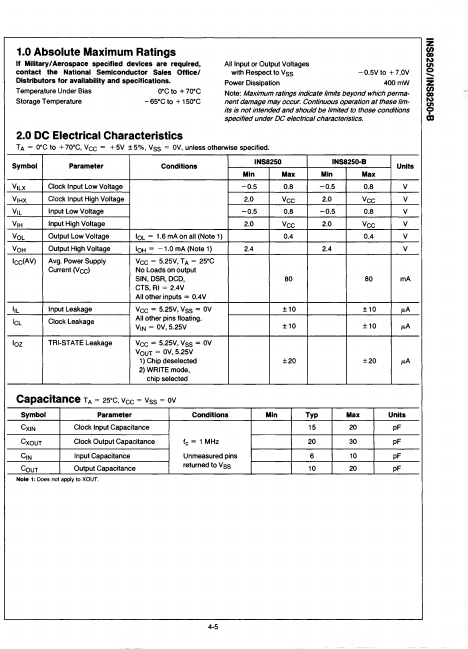
INS8250-B Overview
Each of these parts function as a serial data input/output interface in a microputer system. The system software determines the functional configuration of the UART via a TRI-STATE® 8-bit bidirectional data bus. The UART performs serial-to-parallel conversion on data characters received from a peripheral device or a MODEM, and parallel-to-serial conversion on data characters re ceived from the CPU.
INS8250-B Key Features
- Easily interfaces to most popular microprocessors
- Adds or deletes standard asynchronous munication
- Holding and shift registers eliminate the need for pre cise synchronization between the CPU and the serial data
- Independently controlled transmit, receive, line status, and data set interrupts
- Programmable baud generator allows division of any in put clock by 1 to (216
- 1) and generates the internal 16 x clock
- Independent receiver clock input
- MODEM control functions (CTS, RTS, DSR, DTR, Rl
- Fully programmable serial-interface characteristics
- 5-, 6-, 7-, or 8-bit characters