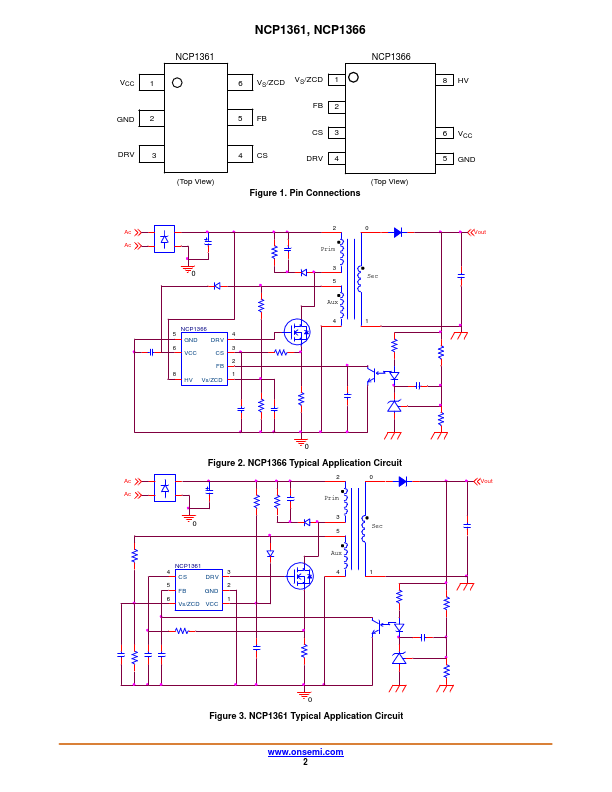
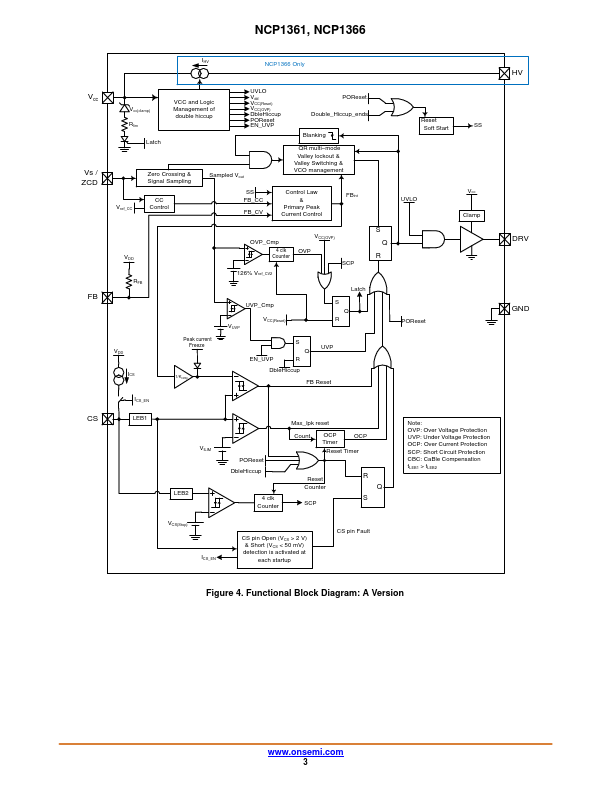
NCP13616 Description
Low Power Offline Constant Current PWM Current-Mode Controller with/without High Voltage Startup Current Source NCP1361, NCP1366 The NCP1361/66 offers a new solution targeting output power levels from a few watts up to 20 W in a universal−mains flyback application. Due to a novel method this new controller offers a primary−side constant current control, saving secondary−side ponents to perform current regulation....
NCP13616 Key Features
- ±10% Current Regulation
- 560 V Startup Current Source
- No Frequency Clamp, 80 or 110 kHz Maximum Switching
- Quasi-Resonant Operation with Valley Switching Operation
- Fixed Peak Current & Deep Frequency Foldback @ Light Load
- External Constant Voltage Feedback Adjustment
- Cycle by Cycle Peak Current Limit
- Built-In Soft-Start
- Over & Under Output Voltage Protection
- Wide Operation VCC Range (up to 28 V)
NCP13616 Applications
- Low power ac−dc Adapters for Chargers
- Ac−dc USB chargers for Cell Phones, Tablets and Cameras