UCC2921 Overview
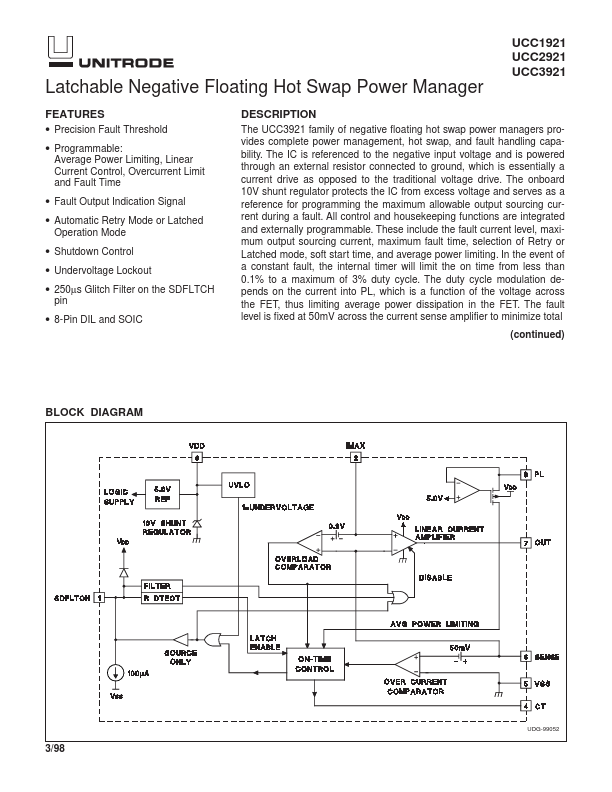
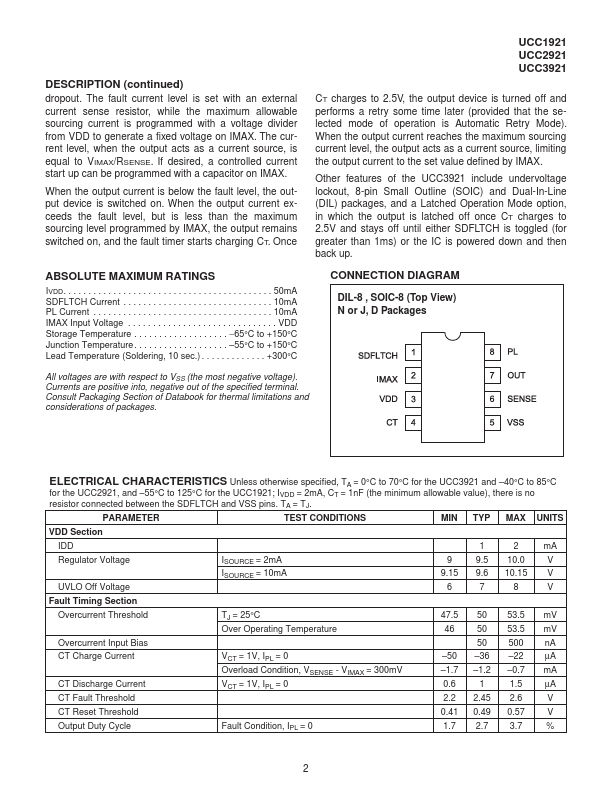
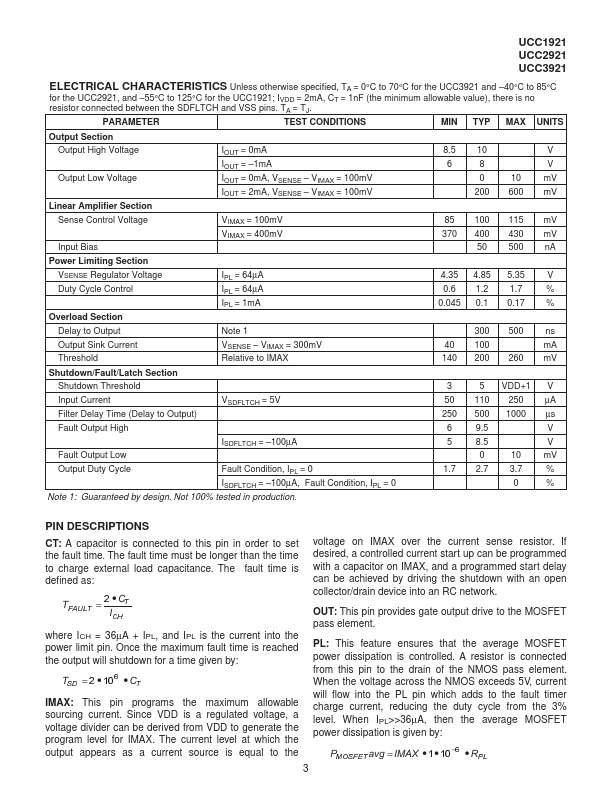
The UCC3921 family of negative floating hot swap power managers provides plete power management, hot swap, and fault handling capability. The IC is referenced to the negative input voltage and is powered through an external resistor connected to ground, which is essentially a current drive as opposed to the traditional voltage drive. The onboard 10V shunt regulator protects the IC from excess voltage and serves as a...
UCC2921 Key Features
- Precision Fault Threshold
- Programmable: Average Power Limiting, Linear Current Control, Overcurrent Limit and Fault Time
- Fault Output Indication Signal
- Automatic Retry Mode or Latched Operation Mode
- Shutdown Control
- Undervoltage Lockout
- 250µs Glitch Filter on the SDFLTCH pin
- 8-Pin DIL and SOIC