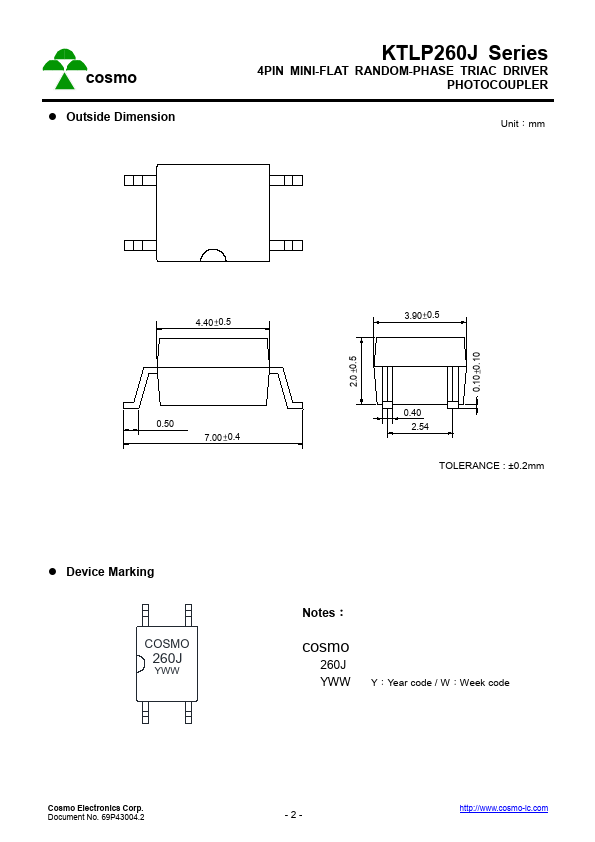
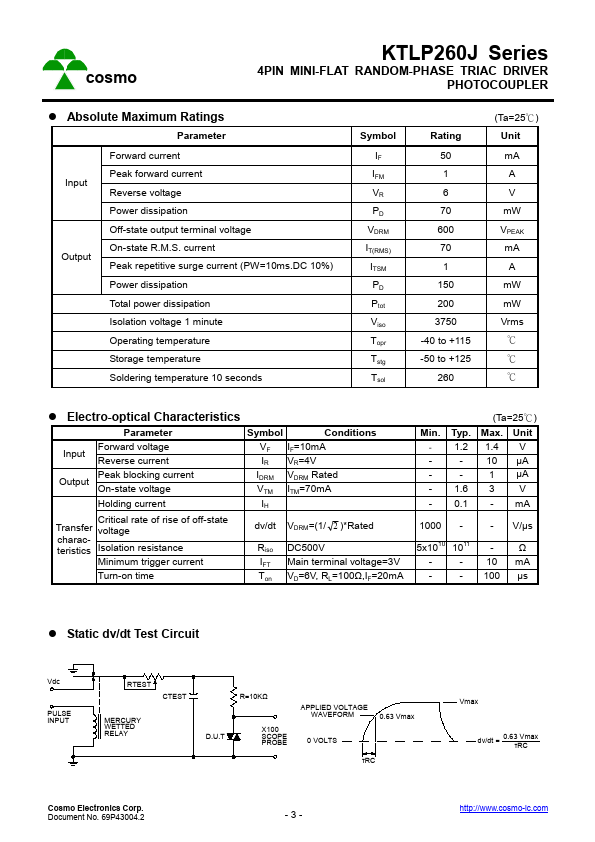
KTLP260J Overview
The KTLP260J series consist of a GaAs infrared emitting diode optically coupled to a non-zero-crossing silicon bilateral AC switch (TRIAC). These devices isolate low voltage logic from 115/240 VAC lines to provide random phase control of high current TRIACs or thyristors.
KTLP260J Key Features
- UL Approved (No. E169586): UL1577
- C-UL Approved (No. E169586)
- VDE Approv