74LCXZ245 Description
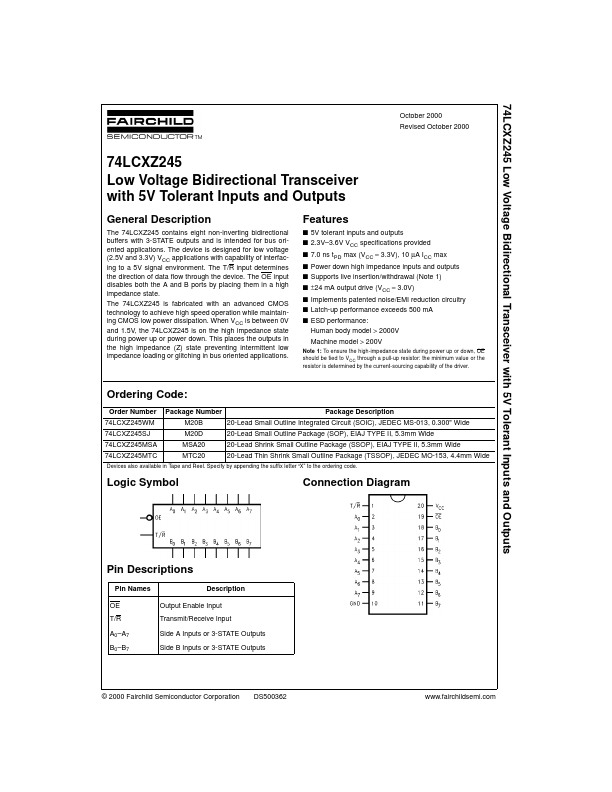
The 74LCXZ245 contains eight non-inverting bidirectional buffers with 3-STATE outputs and is intended for bus oriented applications. The device is designed for low voltage (2.5V and 3.3V) VCC applications with capability of interfacing to a 5V signal environment. The T/R input determines the direction of data flow through the device.
74LCXZ245 Key Features
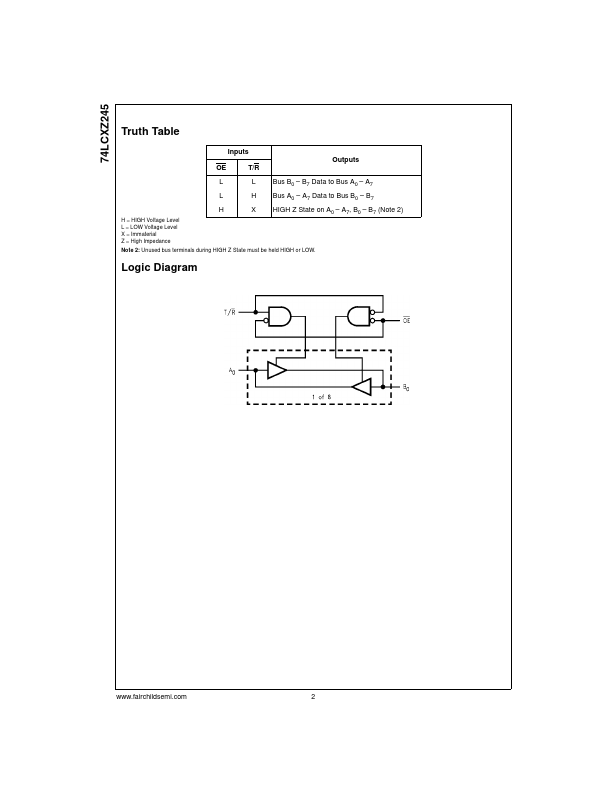
- B7 Data to Bus A0
- A7 Bus A0
- A7 Data to Bus B0
- B7 HIGH Z State on A0
- A7, B0
- B7 (Note 2)