MB8117-12 Description
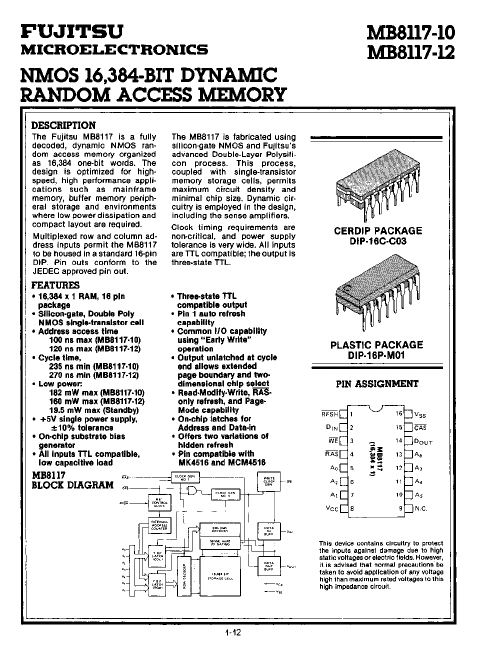
The Fujitsu MB8117 is a fully decoded, dynamic NMOS random access memory organized as 16,384 one-bit words. The design is optimized for highspeed, high performance applications such as mainframe memory, buffer memory peripheral storage and environments where low power dissipation and pact layout are required. Multiplexed row and column address inputs permit the MB8117 to be housed in a standard 16-pin DIP.
MB8117-12 Key Features
- 16,384 x 1 RAM, 16 pin package
- Address access time 100 ns max (MB8117-10) 120 ns max (MB8117-12)
- Cycle time, 235 ns min (MB8117-10) 270 ns min (MB8117-12)
- +5V single power supply, :t 10% tolerance
- On-chip substrate bias generator
- All Inputs TTL patible, low capacitive load
- Thre.state TTL patible output
- Pin 1 auto refresh capability
- mon 110 capability using "Early Write" operation
- Output unlatched at cycle end allows extended