74HCT4020-Q100 Overview
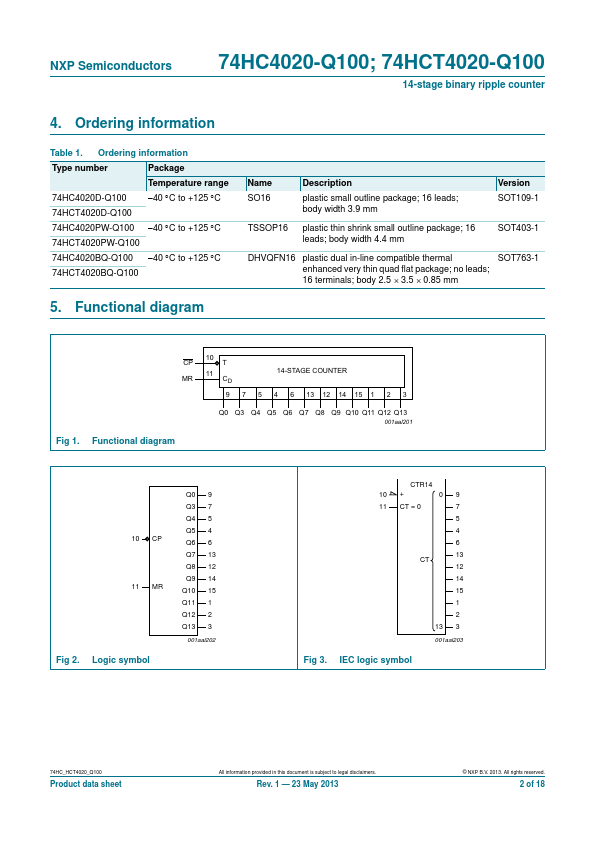
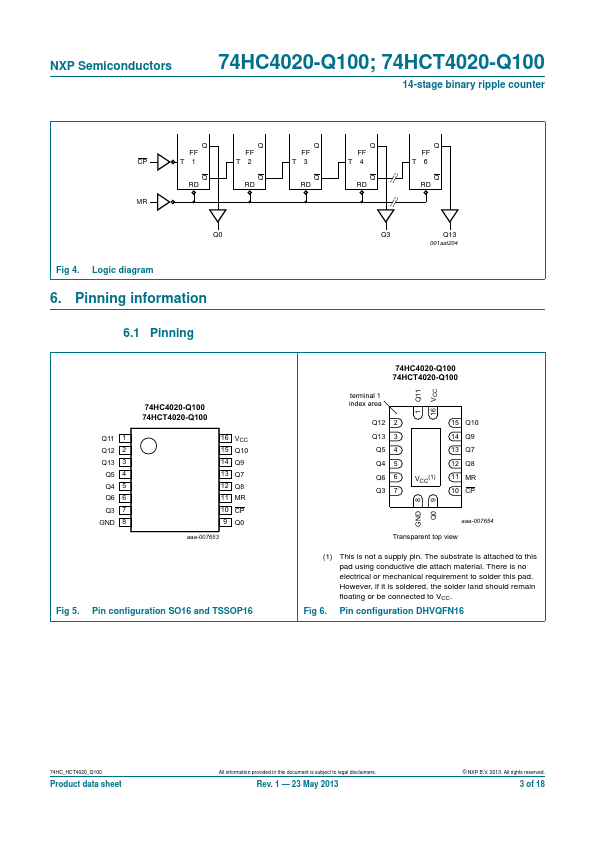
74HCT4020-Q100 are 14-stage binary ripple counters with a clock input (CP), an overriding asynchronous master reset input (MR) and 12 buffered parallel outputs (Q0, and Q3 to Q13). The counter advances on the HIGH-to-LOW transition of CP. A HIGH on MR clears all counter stages and forces all outputs LOW, independent of the state of CP.
74HCT4020-Q100 Key Features
- Automotive product qualification in accordance with AEC-Q100 (Grade 1)
- Specified from 40 C to +85 C and from 40 C to +125 C
- Input levels
- For 74HC4020-Q100: CMOS level
- For 74HCT4020-Q100: TTL level
- plies with JEDEC standard no. 7A
- ESD protection
- MIL-STD-883, method 3015 exceeds 2000 V
- HBM JESD22-A114F exceeds 2000 V
- MM JESD22-A115-A exceeds 200 V (C = 200 pF, R = 0 )
74HCT4020-Q100 Applications
- Automotive product qualification in accordance with AEC-Q100 (Grade 1) Specified from 40 C to +85 C and from 40 C to +125 C