DP8430V Description
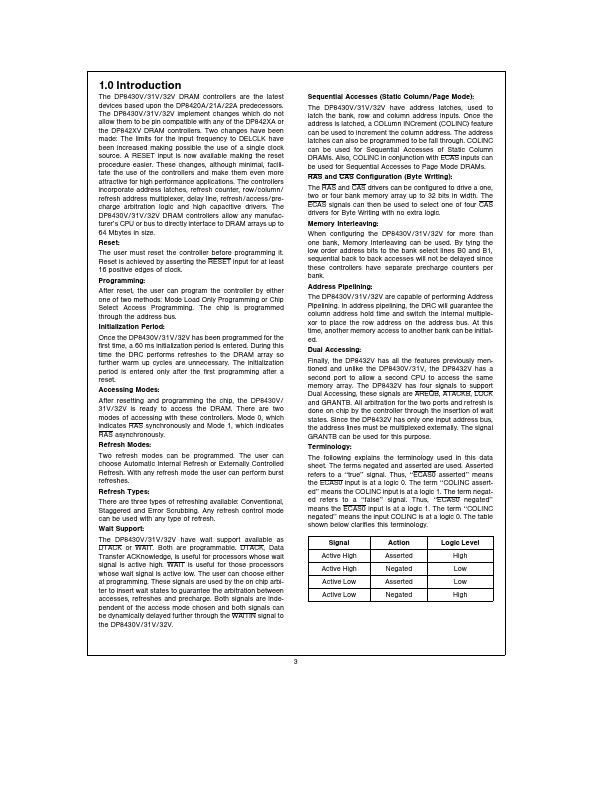
The DP8430V 31V 32V dynamic RAM controllers provide a low cost single chip interface between dynamic RAM and all 8- 16- and 32-bit systems The DP8430V 31V 32V generate all the required access control signal timing for DRAMs An on-chip refresh request clock is used to automatically refresh the DRAM array Refreshes and accesses are arbitrated on chip If necessary a WAIT or DTACK output inserts wait states into system...