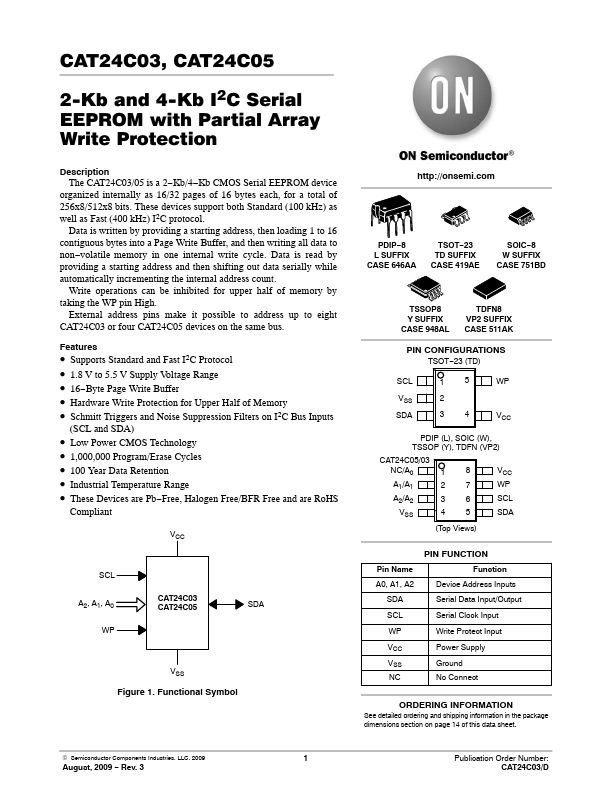
CAT24C05 Description
These devices support both Standard (100 kHz) as well as Fast (400 kHz) I2C protocol. Data is written by providing a starting address, then loading 1 to 16 contiguous bytes into a Page Write Buffer, and then writing all data to non−volatile memory in one internal write cycle. Data is read by providing a starting address and then shifting out data serially while automatically incrementing the internal address count.
CAT24C05 Key Features
- Supports Standard and Fast I2C Protocol
- 1.8 V to 5.5 V Supply Voltage Range
- 16-Byte Page Write Buffer
- Hardware Write Protection for Upper Half of Memory
- Schmitt Triggers and Noise Suppression Filters on I2C Bus Inputs
- Low Power CMOS Technology
- 1,000,000 Program/Erase Cycles
- 100 Year Data Retention
- Industrial Temperature Range
- These Devices are Pb-Free, Halogen Free/BFR Free and are RoHS