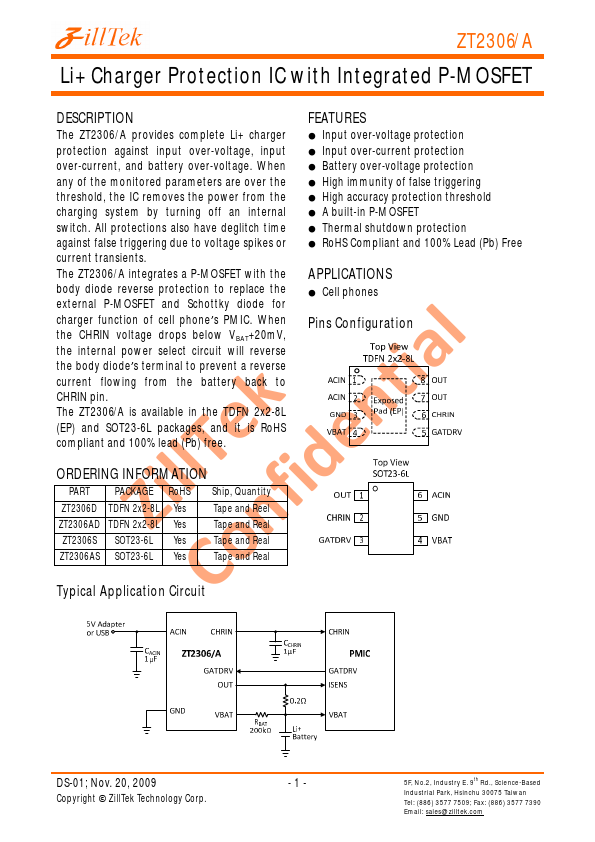
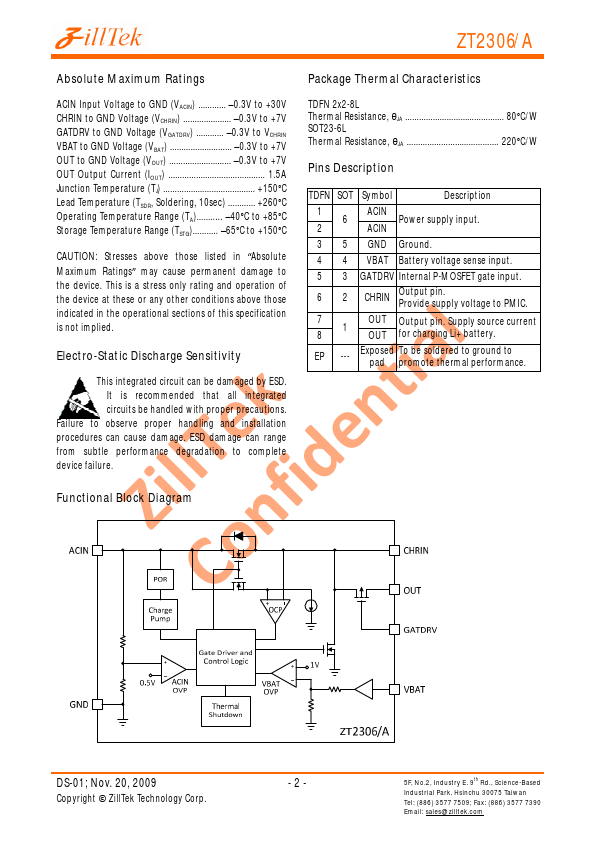
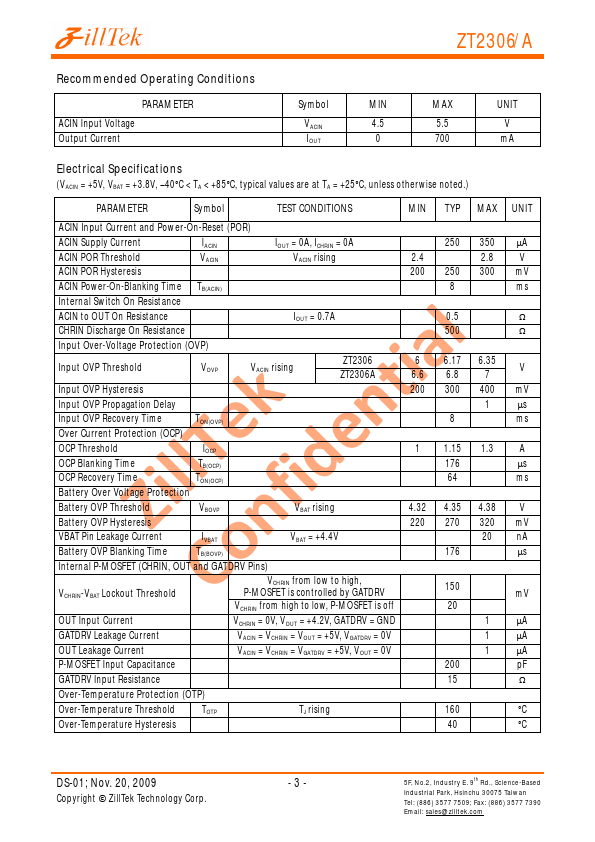
ZT2306A Description
FEATURES The ZT2306/A provides plete Li+ charger Input over-voltage protection protection against input over-voltage, input Input over-current protection over-current, and battery over-voltage. When Battery over-voltage protection any of the monitored parameters are over the High immunity of false triggering threshold, the IC removes the power from the High accuracy protection threshold charging system by turning...
ZT2306A Key Features
- Input over-voltage protection
- Input over-current protection
- Battery over-voltage protection
- High immunity of false triggering
- High accuracy protection threshold
- A built-in P-MOSFET
- Thermal shutdown protection
- RoHS pliant and 100% Lead (Pb) Free