74HCT175D Description
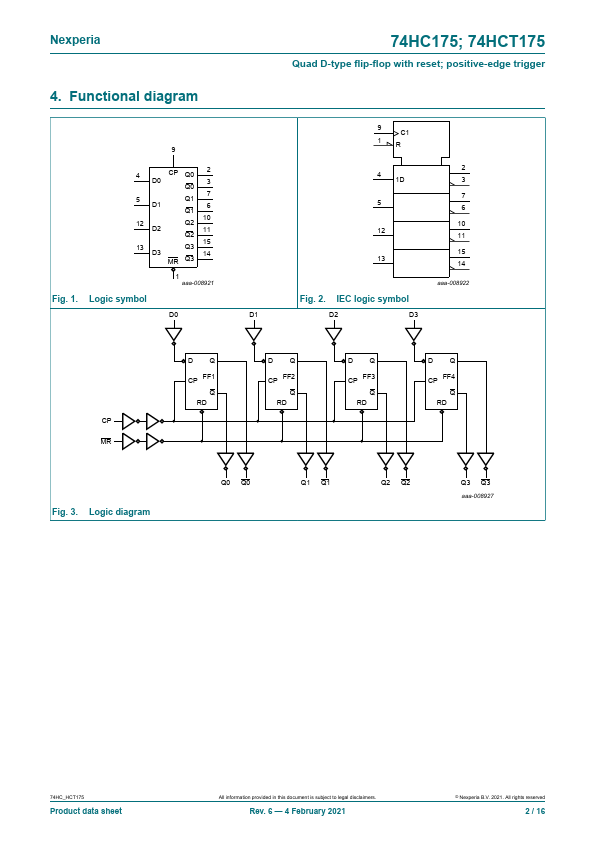
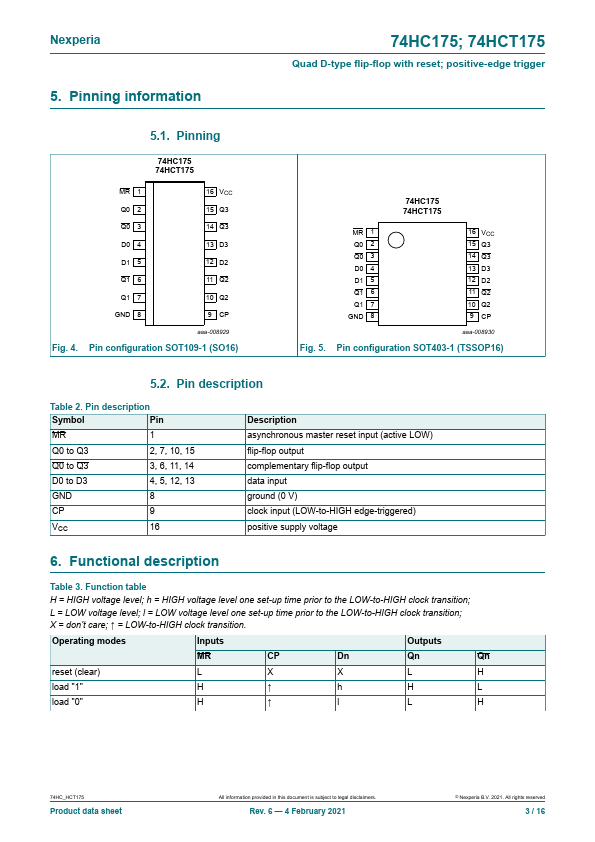
74HCT175 is a quad positive-edge triggered D-type flip-flop with individual data inputs (Dn) and plementary outputs (Qn and Qn). The mon clock (CP) and master reset (MR) inputs load and reset all flip-flops simultaneously. The D-input that meets the set-up and hold time requirements on the LOW-to-HIGH clock transition will be stored in the flip-flop and appear at the Q output.
74HCT175D Key Features
- Input levels
- For 74HC175: CMOS level
- For 74HCT175: TTL level
- Four edge-triggered D-type flip-flops
- Asynchronous master reset
- plies with JEDEC standard no. 7A
- ESD protection
- HBM JESD22-A114F exceeds 2000 V
- MM JESD22-A115-A exceeds 200 V
- Specified from -40 °C to +85 °C and -40 °C to +125 °C