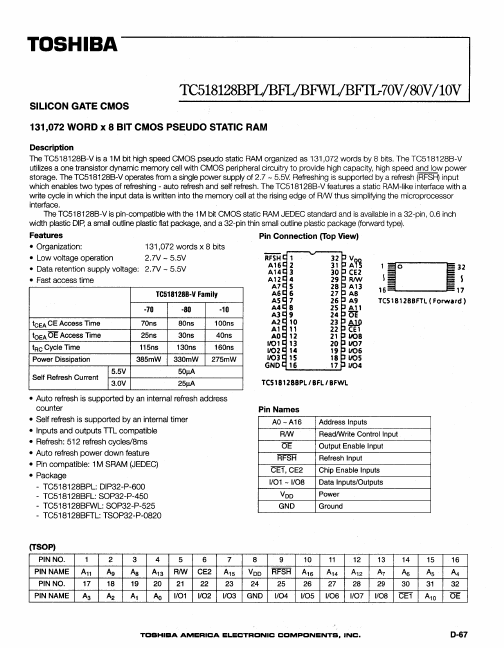
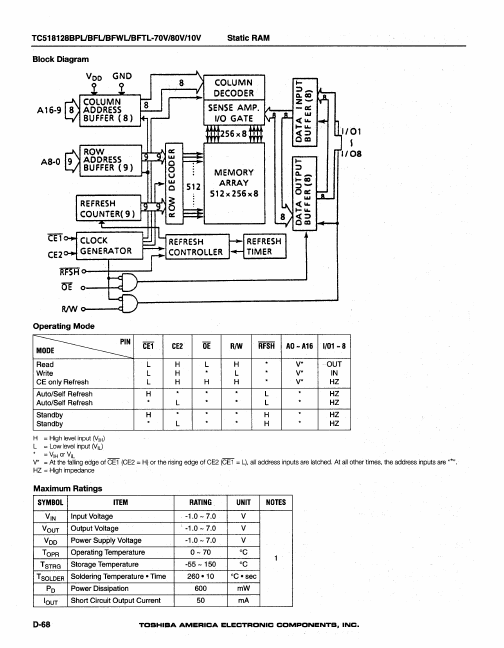
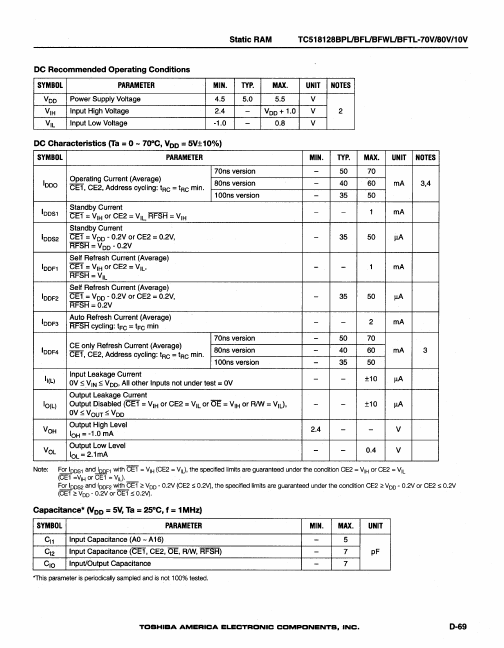
TC518128BFL-10V Description
The TC518128B-V is a 1M bit high speed CMOS pseudo static RAM organized as 131,072 words by 8 bits. The TC518128B-V utilizes a one transistor dynamic memory cell with CMOS peripheral circuitry to provide high capacity, high speed and low power storage. The TC518128B-Voperates from a single power supply of 2.7 - 5.5V.