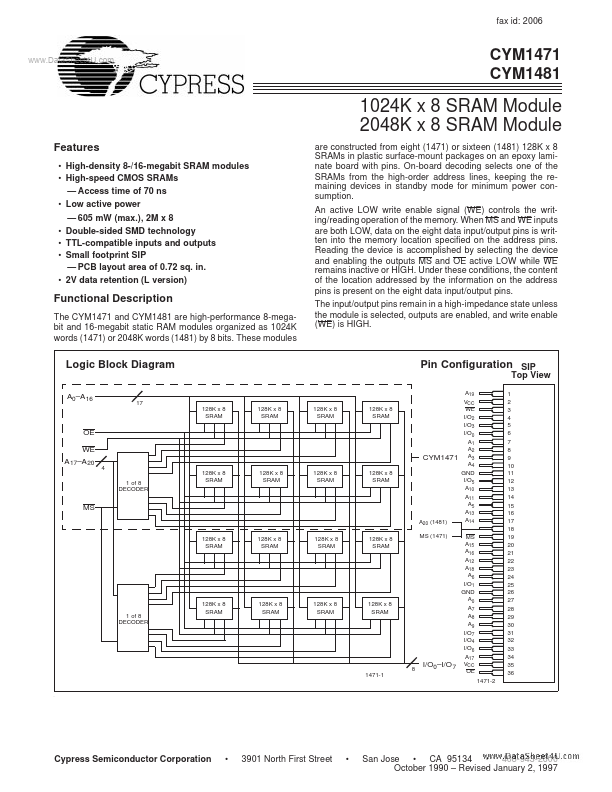
CYM1481 Description
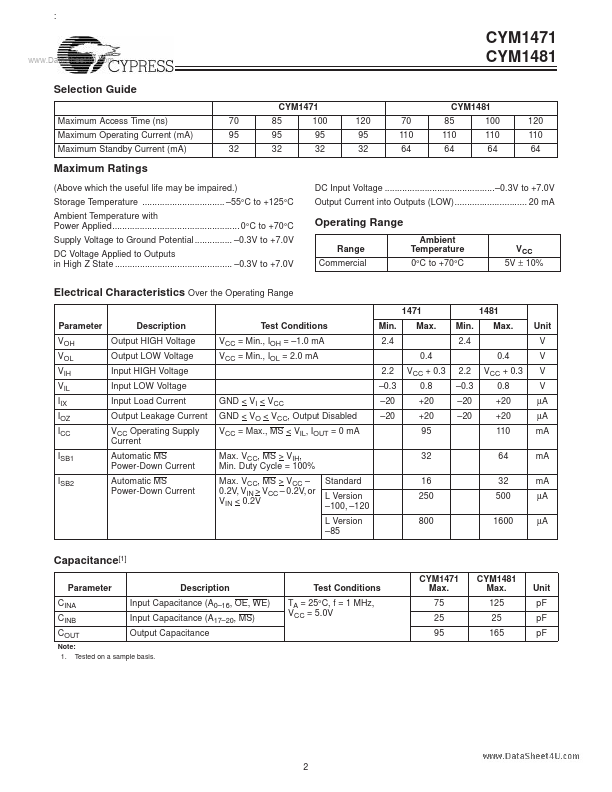
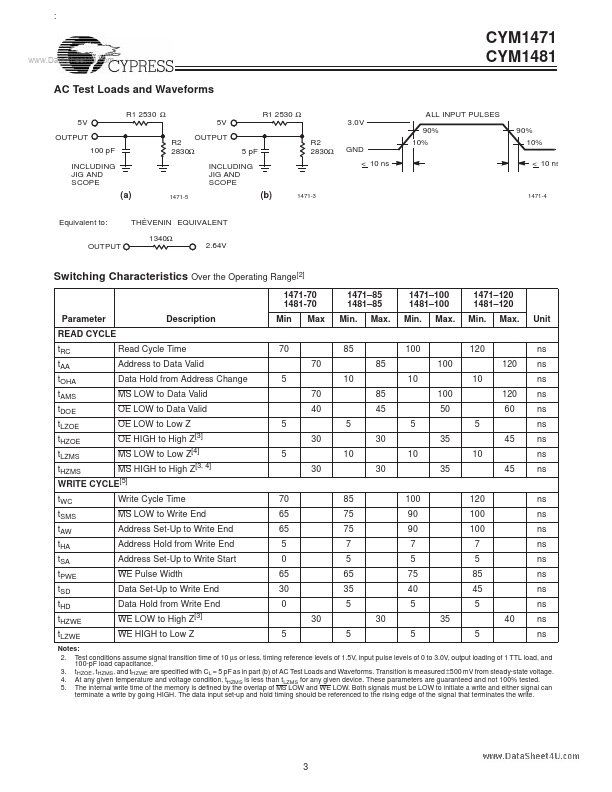
The CYM1471 and CYM1481 are high-performance 8-megabit and 16-megabit static RAM modules organized as 1024K words (1471) or 2048K words (1481) by 8 bits. 55°C to +125°C Ambient Temperature with Power Applied................................................... 0°C to +70°C Supply Voltage to Ground Potential ...............
CYM1481 Key Features
- High-density 8-/16-megabit SRAM modules
- High-speed CMOS SRAMs
- Access time of 70 ns
- Low active power
- 605 mW (max.), 2M x 8
- Double-sided SMD technology
- TTL-patible inputs and outputs
- Small footprint SIP
- 2V data retention (L version) are constructed from eight (1471) or sixteen (1481) 128K x 8 SRAMs in plastic surface-moun