M5M4V64S40ATP-8L Overview
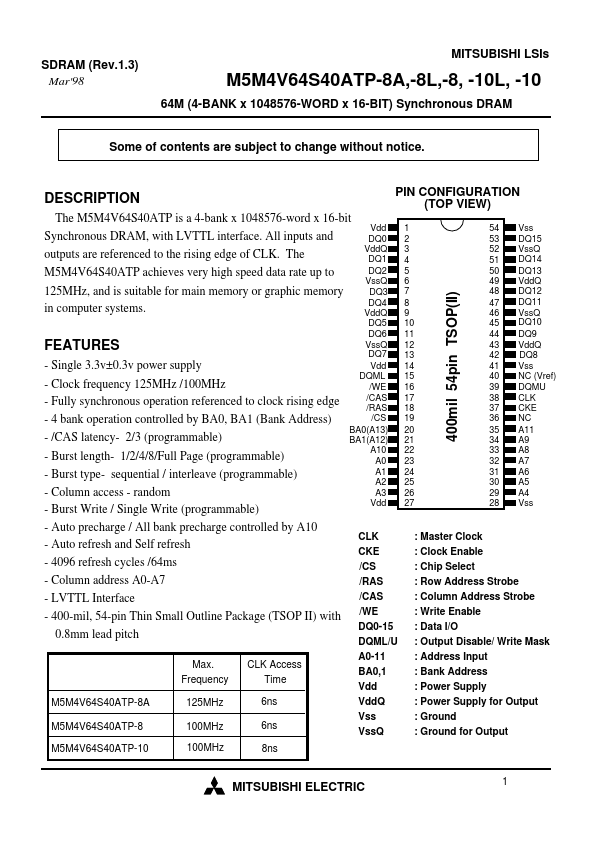
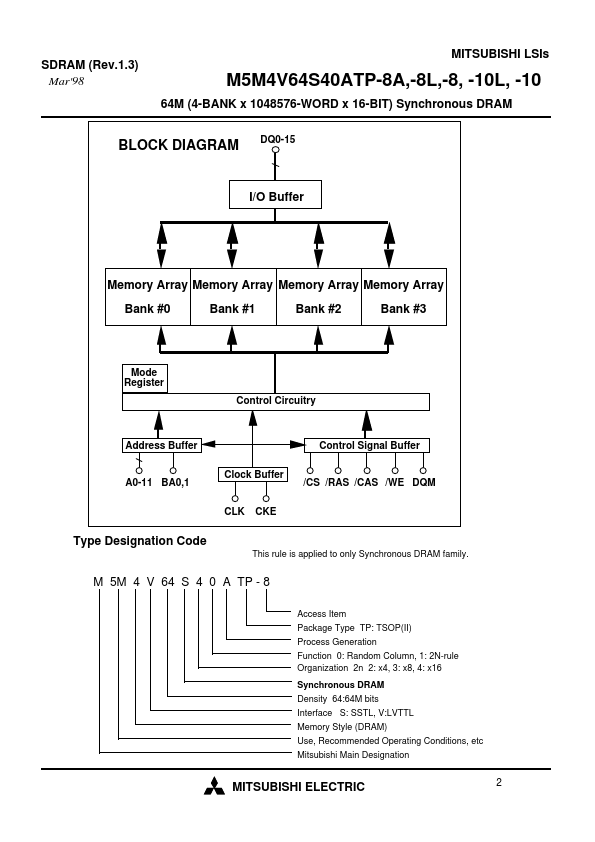
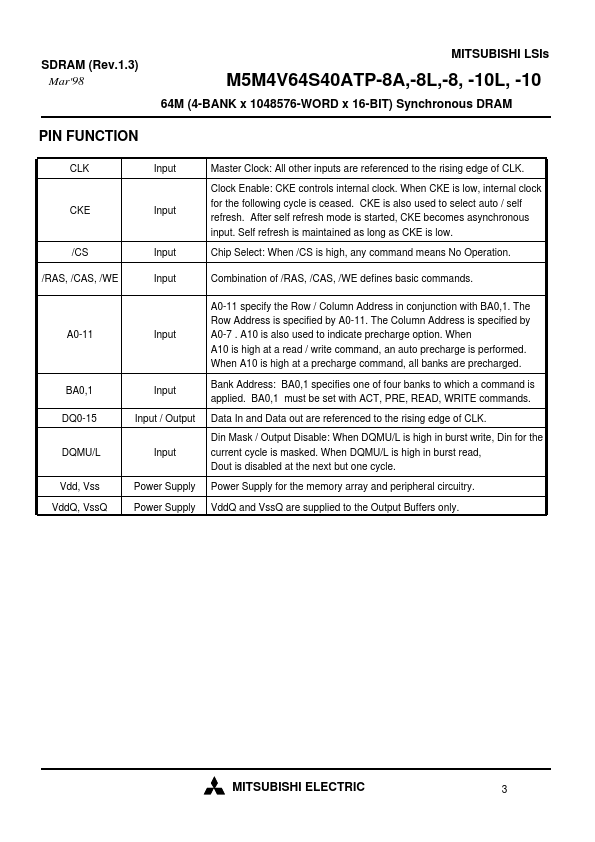
The M5M4V64S40ATP is a 4-bank x 1048576-word x 16-bit Synchronous DRAM, with LVTTL interface. All inputs and outputs are referenced to the rising edge of CLK. The M5M4V64S40ATP achieves very high speed data rate up to 125MHz, and is suitable for main memory or graphic memory in puter systems.
M5M4V64S40ATP-8L Key Features
- Single 3.3v±0.3v power supply
- Clock frequency 125MHz /100MHz
- Fully synchronous operation referenced to clock rising edge
- 4 bank operation controlled by BA0, BA1 (Bank Address)
- /CAS latency- 2/3 (programmable)
- Burst length- 1/2/4/8/Full Page (programmable)
- Burst type- sequential / interleave (programmable)
- Column access
- random
- Burst Write / Single Write (programmable)