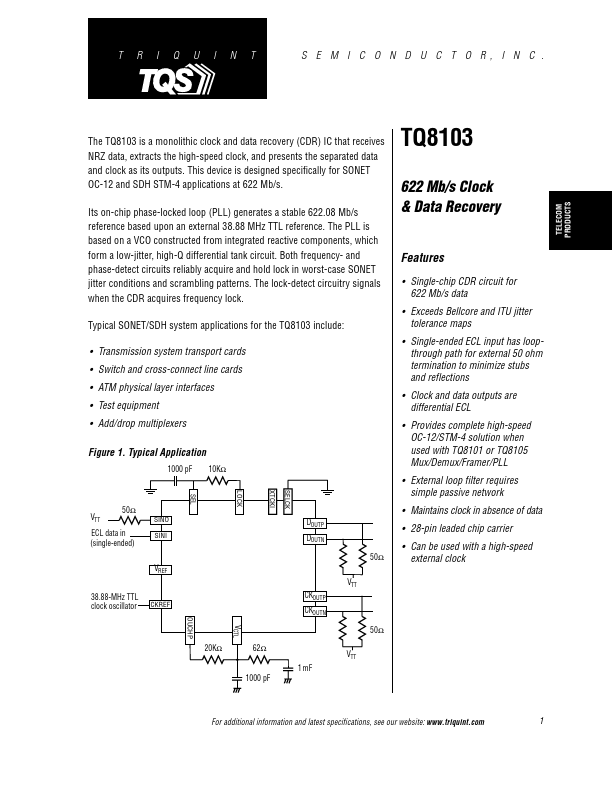
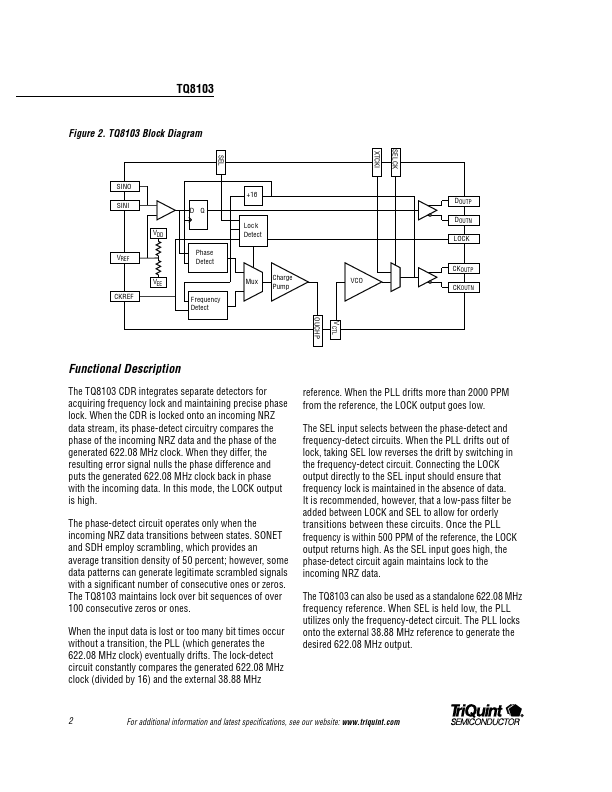
TQ8103 Description
The TQ8103 CDR integrates separate detectors for acquiring frequency lock and maintaining precise phase lock. When the CDR is locked onto an ining NRZ data stream, its phase-detect circuitry pares the phase of the ining NRZ data and the phase of the generated 622.08 MHz clock. When they differ, the resulting error signal nulls the phase difference and puts the generated 622.08 MHz clock back in phase with the ining...
TQ8103 Key Features
- Single-chip CDR circuit for 622 Mb/s data
- Exceeds Bellcore and ITU jitter tolerance maps
- Single-ended ECL input has loopthrough path for external 50 ohm termination to minimize stubs and reflections
- Clock and data outputs are differential ECL
- Provides plete high-speed OC-12/STM-4 solution when used with TQ8101 or TQ8105 Mux/Demux/Framer/PLL
- External loop filter requires simple passive network
- Maintains clock in absence of data
- Transmission system transport cards
- Switch and cross-connect line cards
- ATM physical layer interfaces
TQ8103 Applications
- Single-chip CDR circuit for 622 Mb/s data