IRF7475PBF Description
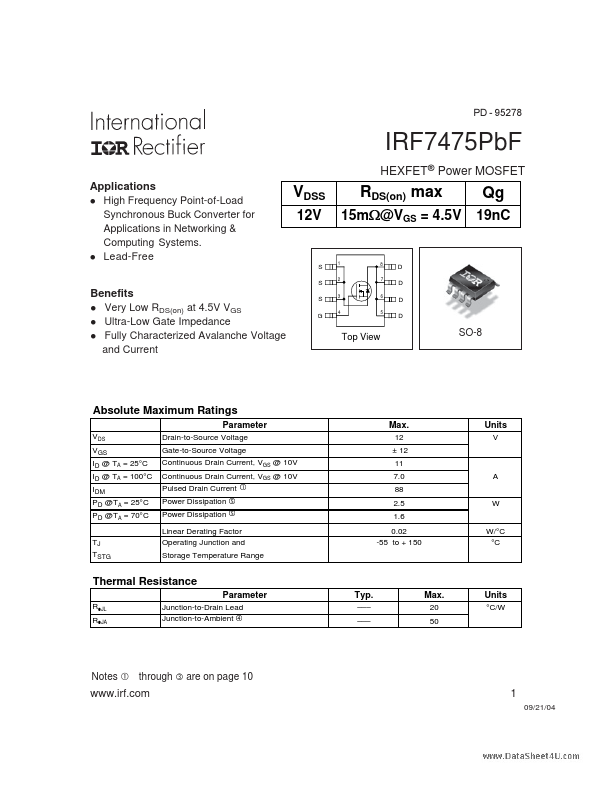
PD - 95278 IRF7475PbF HEXFET® Power MOSFET Applications l High Frequency Point-of-Load Synchronous Buck Converter for Applications in Networking & puting Systems. 12 ± 12 11 7.0 88 2.5 1.6 0.02 -55 to + 150 Units V g Power Dissipation g Power Dissipation c A W Linear Derating Factor Operating Junction and Storage Temperature Range W/°C °C Parameter RθJL RθJA Junction-to-Drain Lead Junction-to-Ambient Typ. 20 50...
IRF7475PBF Key Features
- High Frequency Point-of-Load Synchronous Buck Converter for Applications in Networking & puting Systems
- Lead-Free Benefits
- Very Low RDS(on) at 4.5V VGS
- Ultra-Low Gate Impedance
- Fully Characterized Avalanche Voltage and Current VDSS 12V 15m:@VGS = 4.5V 1 8 7 RDS(on) max Qg 19nC S S