CY7C1321KV18 Overview
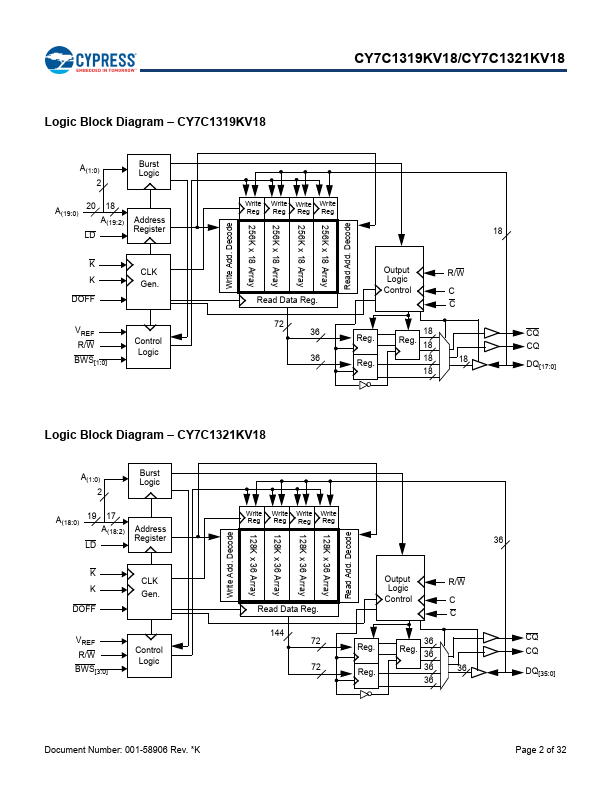
CY7C1319KV18 and CY7C1321KV18 are 1.8 V Synchronous Pipelined SRAMs equipped with DDR II architecture. The DDR II consists of an SRAM core with advanced synchronous peripheral circuitry and a two-bit burst counter. Addresses for read and write are latched on alternate rising edges of the input (K) clock.
CY7C1321KV18 Key Features
- 18-Mbit density (1M × 18, 512K × 36)
- 333-MHz clock for high bandwidth
- Four-word burst for reducing address bus frequency
- Double data rate (DDR) interfaces (data transferred at
- Two input clocks (K and K) for precise DDR timing
- SRAM uses rising edges only
- Two input clocks for output data (C and C) to minimize clock
- Echo clocks (CQ and CQ) simplify data capture in high speed
- Synchronous internally self-timed writes
- DDR II operates with 1.5 cycle read latency when DOFF is